Comparative genome analysis of Vibrio vulnificus, a marine pathogen
- PMID: 14656965
- PMCID: PMC403799
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.1295503
Comparative genome analysis of Vibrio vulnificus, a marine pathogen
Abstract
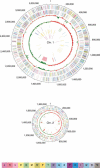
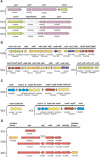
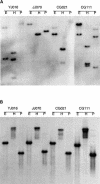
The halophile Vibrio vulnificus is an etiologic agent of human mortality from seafood-borne infections. We applied whole-genome sequencing and comparative analysis to investigate the evolution of this pathogen. The genome of biotype 1 strain, V. vulnificus YJ016, was sequenced and includes two chromosomes of estimated 3377 kbp and 1857 kbp in size, and a plasmid of 48,508 bp. A super-integron (SI) was identified, and the SI region spans 139 kbp and contains 188 gene cassettes. In contrast to non-SI sequences, the captured gene cassettes are unique for any given Vibrio species and are highly variable among V. vulnificus strains. Multiple rearrangements were found when comparing the 5.3-Mbp V. vulnificus YJ016 genome and the 4.0-Mbp V. cholerae El Tor N16961 genome. The organization of gene clusters of capsular polysaccharide, iron metabolism, and RTX toxin showed distinct genetic features of V. vulnificus and V. cholerae. The content of the V. vulnificus genome contained gene duplications and evidence of horizontal transfer, allowing for genetic diversity and function in the marine environment. The genomic information obtained in this study can be applied to monitoring vibrio infections and identifying virulence genes in V. vulnificus.
Figures



References
-
- Blake, P.A., Merson, M.H., Weaver, R.E., Hollis, D.G., and Heublein, P.C. 1979. Disease caused by a marine Vibrio. Clinical characteristics and epidemiology. N. Engl. J. Med. 300: 1-5. - PubMed
-
- Borodovsky, M. and McIninch, J.D. 1993. Genemark: Parallel gene recognition for both DNA strands. Comput. Chem. 17: 123-133.
-
- Chuang, Y.C., Yuan, C.Y., Liu, C.Y., Lan, C.K., and Huang, A.H. 1992. Vibrio vulnificus infection in Taiwan: Report of 28 cases and review of clinical manifestations and treatment. Clin. Infect. Dis. 15: 271-276. - PubMed
-
- Collis, C.M., Kim, M.J., Stokes, H.W., and Hall, R.M. 1998. Binding of the purified integron DNA integrase Intl1 to integron- and cassette-associated recombination sites. Mol. Microbiol. 29: 477-490. - PubMed
-
- Coote, J.G. 1992. Structural and functional relationships among the RTX toxin determinants of gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 8: 137-161. - PubMed
WEB SITE REFERENCES
-
- http://genome.nhri.org.tw/vv/; Vibrio vulnificus YJ016 Web site with online supplemental information.
-
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/COG/; The NCBI COG database; the database of Clusters of Orthologous Groups of proteins.
-
- http://genome.ym.edu.tw/; National Yang Ming University Genome Research Center.
-
- http://www.bmec.itri.org.tw/; Biomedical Engineering Center, Industrial Technology Research Institute.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
