Analysis of the gene-dense major histocompatibility complex class III region and its comparison to mouse
- PMID: 14656967
- PMCID: PMC403804
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.1736803
Analysis of the gene-dense major histocompatibility complex class III region and its comparison to mouse
Abstract
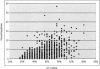
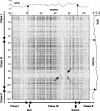
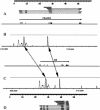
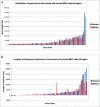
In mammals, the Major Histocompatibility Complex class I and II gene clusters are separated by an approximately 700-kb stretch of sequence called the MHC class III region, which has been associated with susceptibility to numerous diseases. To facilitate understanding of this medically important and architecturally interesting portion of the genome, we have sequenced and analyzed both the human and mouse class III regions. The cross-species comparison has facilitated the identification of 60 genes in human and 61 in mouse, including a potential RNA gene for which the introns are more conserved across species than the exons. Delineation of global organization, gene structure, alternative splice forms, protein similarities, and potential cis-regulatory elements leads to several conclusions: (1) The human MHC class III region is the most gene-dense region of the human genome: >14% of the sequence is coding, approximately 72% of the region is transcribed, and there is an average of 8.5 genes per 100 kb. (2) Gene sizes, number of exons, and intergenic distances are for the most part similar in both species, implying that interspersed repeats have had little impact in disrupting the tight organization of this densely packed set of genes. (3) The region contains a heterogeneous mixture of genes, only a few of which have a clearly defined and proven function. Although many of the genes are of ancient origin, some appear to exist only in mammals and fish, implying they might be specific to vertebrates. (4) Conserved noncoding sequences are found primarily in or near the 5'-UTR or the first intron of genes, and seldom in the intergenic regions. Many of these conserved blocks are likely to be cis-regulatory elements.
Figures


References
-
- Abi-Rached, L., Gilles, A., Shiina, T., Pontarotti, P., and Inoko, H. 2002. Evidence of en bloc duplication in vertebrate genomes. Nat. Genet. 31: 100-105. - PubMed
-
- Aguado, B. and Campbell, R.D. 1998. Characterization of a human lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase that is encoded by a gene located in the class III region of the human major histocompatibility complex. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 4096-4105. - PubMed
-
- Albig, W. and Doenecke, D. 1997. The human histone gene cluster at the D6S105 locus. Hum. Genet. 101: 284-294. - PubMed
-
- Ansari-Lari, M.A., Muzny, D.M., Lu, J., Lu, F., Lilley, C.E., Spanos, S., Malley, T., and Gibbs, R.A. 1996. A gene-rich cluster between the CD4 and triosephosphate isomerase genes at human chromosome 12p13. Genome Res. 6: 314-326. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio, S., Chapman, J., Stupka, E., Putnam, N., Chia, J.M., Dehal, P., Christoffels, A., Rash, S., Hoon, S., Smit, A., et al. 2002. Whole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Fugu rubripes. Science 297: 1301-1310. - PubMed
WEB SITE REFERENCES
-
- http://bio.math.berkeley.edu/avid/; AVID program.
-
- http://db.systemsbiology.net/projects/local/mhc/SNP/; comparison of SNPs.
-
- http://db.systemsbiology.net/projects/mhc/acgt/; ACGT (A Comparative Genomics Tool). - PubMed
-
- http://genome.cse.ucsc.edu; GoldenPath assembly.
-
- http://rast.abajian.com/sputnik/; Sputnik program.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
