Transcriptional activation of known and novel apoptotic pathways by Nur77 orphan steroid receptor
- PMID: 14657025
- PMCID: PMC291815
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg620
Transcriptional activation of known and novel apoptotic pathways by Nur77 orphan steroid receptor
Abstract
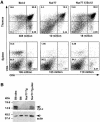
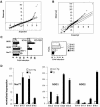
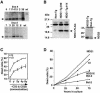
Nur77 is a nuclear orphan steroid receptor that has been implicated in negative selection. Expression of Nur77 in thymocytes and cell lines leads to apoptosis through a mechanism that remains unclear. In some cell lines, Nur77 was reported to act through a transcription-independent mechanism involving translocation to mitochondria, leading to cytochrome c release. However, we show here that Nur77-mediated apoptosis in thymocytes does not involve cytoplasmic cytochrome c release and cannot be rescued by Bcl-2. Microarray analysis shows that Nur77 induces many genes, including two novel genes (NDG1, NDG2) and known apoptotic genes FasL and TRAIL. Characterization of NDG1 and NDG2 indicates that NDG1 initiates a novel apoptotic pathway in a Bcl-2-independent manner. Thus Nur77-mediated apoptosis in T cells involves Bcl-2 independent transcriptional activation of several known and novel apoptotic pathways.
Figures

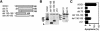

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

