The Mre11 complex is required for ATM activation and the G2/M checkpoint
- PMID: 14657032
- PMCID: PMC291825
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg630
The Mre11 complex is required for ATM activation and the G2/M checkpoint
Abstract
The maintenance of genome integrity requires a rapid and specific response to many types of DNA damage. The conserved and related PI3-like protein kinases, ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and ATM-Rad3-related (ATR), orchestrate signal transduction pathways in response to genomic insults, such as DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). It is unclear which proteins recognize DSBs and activate these pathways, but the Mre11/Rad50/NBS1 complex has been suggested to act as a damage sensor. Here we show that infection with an adenovirus lacking the E4 region also induces a cellular DNA damage response, with activation of ATM and ATR. Wild-type virus blocks this signaling through degradation of the Mre11 complex by the viral E1b55K/E4orf6 proteins. Using these viral proteins, we show that the Mre11 complex is required for both ATM activation and the ATM-dependent G(2)/M checkpoint in response to DSBs. These results demonstrate that the Mre11 complex can function as a damage sensor upstream of ATM/ATR signaling in mammalian cells.
Figures


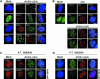
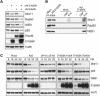
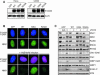
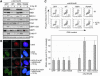

References
-
- Andegeko Y., Moyal,L., Mittelman,L., Tsarfaty,I., Shiloh,Y. and Rotman,G. (2001) Nuclear retention of ATM at sites of DNA double strand breaks. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 38224–38230. - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist C.J. and Kastan,M.B. (2003) DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature, 421, 499–506. - PubMed
-
- Bridge E. and Ketner,G. (1990) Interaction of adenoviral E4 and E1b products in late gene expression. Virology, 174, 345–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

