Cannabinoid CB2 receptors and fatty acid amide hydrolase are selectively overexpressed in neuritic plaque-associated glia in Alzheimer's disease brains
- PMID: 14657172
- PMCID: PMC6741043
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-35-11136.2003
Cannabinoid CB2 receptors and fatty acid amide hydrolase are selectively overexpressed in neuritic plaque-associated glia in Alzheimer's disease brains
Abstract
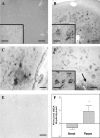
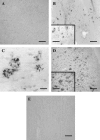
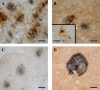
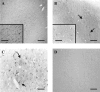
The endocannabinoid system is still poorly understood. Recently, the basic elements that constitute it, i.e., membrane receptors, endogenous ligands, and mechanisms for termination of the signaling process, have been partially characterized. There is a considerable lack of information, however, concerning the distribution, concentration, and function of those components in the human body, particularly during pathological events. We have studied the status of some of the components of the endocannabinoid system, fatty acid amide hydrolase and cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors, in postmortem brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Using specific polyclonal antibodies, we have performed immunohistochemical analysis in hippocampus and entorhinal cortex sections from brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. Our results show that both fatty acid amide hydrolase and cannabinoid CB2 receptors are abundantly and selectively expressed in neuritic plaque-associated astrocytes and microglia, respectively, whereas the expression of CB1 receptors remains unchanged. In addition, the hydrolase activity seems to be elevated in the plaques and surrounding areas. Thus, some elements of the endocannabinoid system may be postulated as possible modulators of the inflammatory response associated with this neurodegenerative process and as possible targets for new therapeutic approaches.
Figures

References
-
- Beltramo M, Piomelli D ( 2000) Carrier-mediated transport and enzymatic hydrolysis of the endogenous cannabinoid 2-arachidonylglycerol. NeuroReport 11: 1231-1235. - PubMed
-
- Breivogel CS, Griffin G, Di Marzo V, Martin BR ( 2001) Evidence for a new G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor in mouse brain. Mol Pharmacol 60: 155-163. - PubMed
-
- Carlisle SJ, Marciano-Cabral F, Staab A, Ludwick C, Cabral GA ( 2002) Differential expression of the CB2 cannabinoid receptor by rodent macrophages and macrophage-like cells in relation to cell activation. Int Immunopharmacol 2: 69-82. - PubMed
-
- Deutsch DG, Glaser ST, Howell JM, Kunz JS, Puffenbarger RA, Hillard CJ, Abumrad N ( 2000) The cellular uptake of anandamide is coupled to its breakdown by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). J Biol Chem 276: 6967-6973. - PubMed
-
- Deutsch DG, Ueda N, Yamamoto S ( 2002) The fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 66: 201-210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
