Translocation of FGF-1 and FGF-2 across vesicular membranes occurs during G1-phase by a common mechanism
- PMID: 14657241
- PMCID: PMC329394
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-08-0589
Translocation of FGF-1 and FGF-2 across vesicular membranes occurs during G1-phase by a common mechanism
Abstract
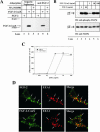
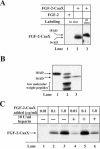
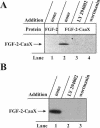
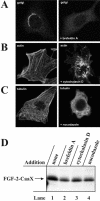
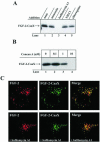
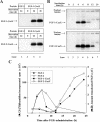
The entry of exogenous fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2) to the cytosolic/nuclear compartment was studied and compared with the translocation mechanism used by FGF-1. To differentiate between external and endogenous growth factor, we used FGF-2 modified to contain a farnesylation signal, a CaaX-box. Because farnesylation occurs only in the cytosol and nucleoplasm, farnesylation of exogenous FGF-2-CaaX was taken as evidence that the growth factor had translocated across cellular membranes. We found that FGF-2 translocation occurred in endothelial cells and fibroblasts, which express FGF receptors, and that the efficiency of translocation was increased in the presence of heparin. Concomitantly with translocation, the 18-kDa FGF-2 was N-terminally cleaved to yield a 16-kDa form. Translocation of FGF-2 required PI3-kinase activity but not transport through the Golgi apparatus. Inhibition of endosomal acidification did not prevent translocation, whereas dissipation of the vesicular membrane potential completely blocked it. The data indicate that translocation occurs from intracellular vesicles containing proton pumps and that an electrical potential across the vesicle membrane is required. Translocation of both FGF-1 and FGF-2 occurred during most of G(1) but decreased shortly before the G(1)-->S transition. A common mechanism for FGF-1 and FGF-2 translocation into cells is postulated.
Figures


References
-
- Arnaud, E., Touriol, C., Boutonnet, C., Gensac, M.C., Vagner, S., Prats, H., and Prats, A.C. (1999). A new 34-kilodalton isoform of human fibroblast growth factor 2 is cap dependently synthesized by using a non-AUG start codon and behaves as a survival factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 505-514. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bailly, K., Soulet, F., Leroy, D., Amalric, F., and Bouche, G. (2000). Uncoupling of cell proliferation and differentiation activities of basic fibroblast growth factor. FASEB J. 14, 333-344. - PubMed
-
- Bomsel, M., Parton, R., Kuznetsov, S.A., Schroer, T.A., and Gruenberg, J. (1990). Microtubule- and motor-dependent fusion in vitro between apical and basolateral endocytic vesicles from MDCK cells. Cell 62, 719-731. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet, H., Filhol, O., Truchet, I., Brethenou, P., Cochet, C., Amalric, F., and Bouche, G. (1996). Fibroblast growth factor-2 binds to the regulatory beta subunit of CK2 and directly stimulates CK2 activity toward nucleolin. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 24781-24787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

