Basolateral amygdala lesions do not prevent memory of context-footshock training
- PMID: 14657260
- PMCID: PMC305464
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.64003
Basolateral amygdala lesions do not prevent memory of context-footshock training
Abstract
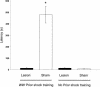
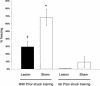
The present studies examined the effects of basolateral amygdala (BLA) lesions induced prior to or after context-footshock training on 48-h memory, using several retention measures. In experiment 1, male Sprague-Dawley rats with bilateral BLA lesions (NMDA, 12.5 mg/mL, 0.2 microL) were given footshock training in one compartment of a two-compartment alley. Rats were habituated to the alley and 24 h later were given two footshocks in the shock compartment. Retention was tested 48 h later, using latency to enter the shock compartment and time spent freezing as measures of memory. Two days later, they were tested again and received a footshock on each re-entry of the shock compartment prior to remaining in the safe compartment for 200 consecutive seconds. The BLA lesions did not block retention as assessed by freezing or number of re-entries of the shock compartment. In experiment 2, no prior habituation was given, and only one footshock was used for the training. BLA lesions did not block retention, as indicated by latencies to enter the shock compartment on a 48-h test or by number of entries of the shock compartment. Experiment 3 examined the effects of the GABAA agonist muscimol infused into the BLA prior to the 48-h retention test. The muscimol infusions decreased retention test entrance latencies but did not block retention as assessed by the number of subsequent entries of the shock compartment. These findings provide additional evidence that an intact BLA is not required for the acquisition or retention of context-footshock training.
Figures







References
-
- Ambrogi-Lorenzini, C., Baldi, E., Bucherelli, C., Giachetti, A., and Tassoni, G. 1991. Effects of nucleus basolateralis amygdalae neurotoxic lesions on some spontaneous activities in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 50: 1215-1219. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard, D.C. and Blanchard, R.J. 1972. Innate and conditioned reactions to threat in rats with amygdaloid lesions. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 81: 281-290. - PubMed
-
- Burns, L.H., Annett, L., Kelley, A.E., Everitt, B.J., and Robbins, T.W. 1996. Effects of lesions to amygdala, ventral subiculum, medial prefrontal cortex, and nucleus accumbens on the reaction to novelty: Implication for limbic-striatal interactions. Behav. Neurosci. 110: 60-73. - PubMed
-
- Cahill, L., Vazdarjanova, A., and Setlow, B. 2000. The basolateral amygdala complex is involved with, but is not necessary for, rapid acquisition of Pavlovian “fear conditioning.” Eur. J. Neurosci. 12: 3044-3050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
