TGF-beta-induced RhoA and p160ROCK activation is involved in the inhibition of Cdc25A with resultant cell-cycle arrest
- PMID: 14657354
- PMCID: PMC307605
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2536483100
TGF-beta-induced RhoA and p160ROCK activation is involved in the inhibition of Cdc25A with resultant cell-cycle arrest
Abstract
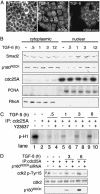
The ability of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) signaling pathways to inhibit proliferation of most cells while stimulating proliferation of others remains a conundrum. In this article, we report that the absence of RhoA and p160ROCK activity in fibroblastic NIH 3T3 cells and its presence in epithelial NMuMG cells can at least partially explain the difference in the TGF-beta growth response. Further, evidence is presented for TGF-beta-stimulated p160ROCK translocation to the nucleus and inhibitory phosphorylation of the cyclin-dependent kinase-activating phosphatase, Cdc25A. The resultant suppression of Cdk2 activity contributes to G1/S inhibition in NMuMG cells. These data provide evidence that signaling through RhoA and p160ROCK is important in TGF-beta inhibition of cell proliferation and links signaling components for epithelial transdifferentiation with regulation of cell-cycle progression.
Figures


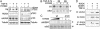

Comment in
-
Another twist in the transforming growth factor beta-induced cell-cycle arrest chronicle.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Dec 23;100(26):15290-1. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307282100. Epub 2003 Dec 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14676328 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

