Xylem wall collapse in water-stressed pine needles
- PMID: 14657404
- PMCID: PMC316319
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.028357
Xylem wall collapse in water-stressed pine needles
Abstract
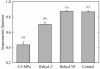
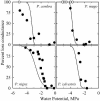
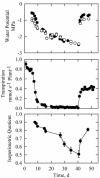
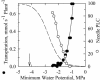
Wall reinforcement in xylem conduits is thought to prevent wall implosion by negative pressures, but direct observations of xylem geometry during water stress are still largely lacking. In this study, we have analyzed the changes in xylem geometry during water stress in needles of four pine species (Pinus spp.). Dehydrated needles were frozen with liquid nitrogen, and xylem cross sections were observed, still frozen, with a cryo-scanning electron microscope and an epifluorescent microscope. Decrease in xylem pressure during drought provoked a progressive collapse of tracheids below a specific threshold pressure (P(collapse)) that correlates with the onset of cavitation in the stems. P(collapse) was more negative for species with smaller tracheid diameter and thicker walls, suggesting a tradeoff between xylem efficiency, xylem vulnerability to collapse, and the cost of wall stiffening. Upon severe dehydration, tracheid walls were completely collapsed, but lumens still appeared filled with sap. When dehydration proceeded further, tracheids embolized and walls relaxed. Wall collapse in dehydrated needles was rapidly reversed upon rehydration. We discuss the implications of this novel hydraulic trait on the xylem function and on the understanding of pine water relations.
Figures


References
-
- Canny MJ (1995) A new theory for the ascent of sap-cohesion supported by tissue pressure. Ann Bot 75: 343-357
-
- Canny MJ (1997) Vessel contents during transpiration: embolisms and refilling. Am J Bot 84: 1223-1230 - PubMed
-
- Cochard H (1992) Vulnerability of several conifers to air embolism. Tree Physiol 11: 73-83 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

