Linkage at 12q24 with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is established and confirmed in Hispanic and European American families
- PMID: 14658095
- PMCID: PMC1181914
- DOI: 10.1086/380913
Linkage at 12q24 with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is established and confirmed in Hispanic and European American families
Abstract
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic, complex, and systemic human autoimmune disease, with both an environmental component and a heritable predisposition. Clinical studies, reinforced by epidemiology and genetics, show impressive variation in disease severity, expression, prevalence, and incidence by ethnicity and sex. To identify the novel SLE susceptibility loci, we performed a genomewide scan with 318 markers on 37 multiplex Hispanic families, using a nonparametric penetrance-independent affected-only allele-sharing method. Three chromosomal regions (12q24, 16p13, and 16q12-21) exceeded our predetermined threshold (Zlr>2.32; nominal P<.01) for further evaluation. Suspected linkages at 12q24, 16p13, and 16q12-21 were tested in an independent data set consisting of 92 European American (EA-1) and 55 African American (AA) families. The linkage at 12q24 was replicated in EA-1 (Zlr=3.06; P=.001) but not in AA (Zlr=0.37; P=.35). Although neither the 16p13 nor the 16q12-21 was confirmed in EA-1 or AA, the suggestive linkage (Zlr=3.06; P=.001) at 16q12-21 is sufficient to confirm the significant linkage, reported elsewhere, at this location. The evidence for linkage at 12q24 in the 129 combined (Hispanic and EA-1) families exceeded the threshold for genomewide significance (Zlr=4.39; P=5.7x10-6; nonparametric LOD=4.19). Parametric linkage analyses suggested a low-penetrance, dominant model (LOD=3.72). To confirm the linkage effect at 12q24, we performed linkage analysis in another set of 82 independent European American families (EA-2). The evidence for linkage was confirmed (Zlr=2.11; P=.017). Therefore, our results have detected, established, and confirmed the existence of a novel SLE susceptibility locus at 12q24 (designated "SLEB4") that may cause lupus, especially in Hispanic and European American families.
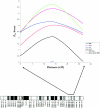
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/
-
- Lupus Multiplex Registry and Repository, http://omrf.ouhsc.edu/
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for SLE) - PubMed
-
- University of California–Santa Cruz Web Site, http://genome.ucsc.edu/ (for Golden Path)
References
-
- Barnes KC, Freidhoff LR, Nickel R, Chiu YF, Juo SH, Hizawa N, Naidu RP, Ehrlich E, Duffy DL, Schou C, Levett PN, Marsh DG, Beaty TH (1999) Dense mapping of chromosome 12q13.12-q23.3 and linkage to asthma and atopy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 104:485–491 - PubMed
-
- Clerget-Darpoux F, Bonaiti-Pellie C, Hochez J (1986) Effects of misspecifying genetic parameters in lod score analysis. Biometrics 42:393–399 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI31584/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR42460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI24717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR012253/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR15577/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR048940/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR048940/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR048928/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI031584/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AR048928/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

