Tolerance to skin and vascularized cardiac allografts using mixed chimerism
- PMID: 1465987
- PMCID: PMC3091366
Tolerance to skin and vascularized cardiac allografts using mixed chimerism
Figures
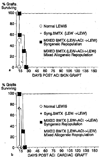
Similar articles
-
Induction of donor-specific transplantation tolerance to skin and cardiac allografts using mixed chimerism in (A + B-->A) in rats.Cell Transplant. 1993 Jul-Aug;2(4):345-53. doi: 10.1177/096368979300200418. Cell Transplant. 1993. PMID: 8162277 Free PMC article.
-
Sublethal irradiation: a nonlethal method to achieve cross-species chimerism (rat-->mouse).Transplant Proc. 1992 Dec;24(6):2866-7. Transplant Proc. 1992. PMID: 1465976 No abstract available.
-
Durable mixed allogeneic chimerism and tolerance by a nonlethal radiation-based cytoreductive approach.J Immunol. 1996 Oct 1;157(7):2820-9. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8816385
-
Induction of tolerance to cardiac allografts by pretreatment with intrathymic UVB donor spleen cells.Transplant Proc. 1992 Dec;24(6):2904-5. Transplant Proc. 1992. PMID: 1465993 No abstract available.
-
Effect of selective depletion of natural killer cells on allograft rejection.Transplant Proc. 1991 Feb;23(1 Pt 1):178-9. Transplant Proc. 1991. PMID: 1990508 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
