Genetic characterization of the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway in Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 and isolation of a colorless mutant
- PMID: 14660416
- PMCID: PMC310018
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.12.7563-7566.2003
Genetic characterization of the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway in Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 and isolation of a colorless mutant
Abstract
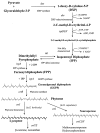
Genomic searches were used to reconstruct the putative carotenoid biosynthesis pathway in the pink-pigmented facultative methylotroph Methylobacterium extorquens AM1. Four genes for putative phytoene desaturases were identified. A colorless mutant was obtained by transposon mutagenesis, and the insertion was shown to be in one of the putative phytoene desaturase genes. Mutations in the other three did not affect color. The tetracycline marker was removed from the original transposon mutant, resulting in a pigment-free strain with wild-type growth properties useful as a tool for future experiments.
Figures
References
-
- Armstrong, G. A., M. Alberti, F. Leach, and J. E. Hearst. 1989. Nucleotide sequence, organization, and nature of the protein products of the carotenoid biosynthesis gene cluster of Rhodobacter capsulatus. Mol. Gen. Genet. 216:254-268. - PubMed
-
- Attwood, M. M., and W. Harder. 1972. A rapid and specific enrichment procedure for Hyphomicrobium spp. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 38:369-377. - PubMed
-
- Barkovich, R., and J. C. Liao. 2001. Metabolic engineering of isoprenoids. Met. Eng. 3:27-39. - PubMed
-
- Bauernfeind, J. C. 1981. Carotenoids as colorants and vitamin A precursors: technological and nutritional applications. Academic Press, Inc., New York, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources