Intraocular pressure after replacement of current dual therapy with latanoprost monotherapy in patients with open angle glaucoma
- PMID: 14660460
- PMCID: PMC1920563
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.87.12.1492
Intraocular pressure after replacement of current dual therapy with latanoprost monotherapy in patients with open angle glaucoma
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of replacing current dual ocular hypotensive therapy with latanoprost 0.005% monotherapy in patients with open angle glaucoma.
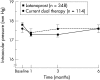
Methods: This randomised, open label, parallel group, multinational study included 466 patients with open angle glaucoma currently on dual ocular hypotensive therapy, including a beta adrenergic receptor antagonist. Patients were assigned (1:3) to ongoing dual therapy or a switch to monotherapy with latanoprost 0.005% once daily for 6 months. Intraocular pressure (IOP) was measured at 10 am and 5 pm at baseline, month 3, and month 6. Groups were compared for differences in diurnal IOP change, IOP success rates (IOP < or =22 mm Hg with < or =15% increase from baseline), and clinical success rates (not requiring change in therapy).
Results: Baseline mean diurnal IOP was 17.8 (SD 2.0) mm Hg in the latanoprost group and 17.6 (2.1) mm Hg in the dual therapy group. After 6 months, mean diurnal IOP was reduced by 0.26 (0.18) (SEM 1.4%) mm Hg (p=0.153) in the group switched to latanoprost and by 0.37 (0.25) (2.1%) mm Hg (p=0.138) in those continuing dual therapy (difference: 0.11 mm Hg; p=0.641). Success rates defined by IOP criteria were 83% for latanoprost and 89% for continued dual therapy (difference: 6%; p=0.122). Clinical success rates were 97% for latanoprost and 99% for dual therapy (difference: 2%; p=0.161). Ocular adverse events were reported by 23% of patients in both treatment groups.
Conclusion: Latanoprost monotherapy is a safe and effective alternative for many patients with open angle glaucoma requiring dual topical ocular hypotensive therapy for IOP control.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Latanoprost : an update of its use in glaucoma and ocular hypertension.Drugs Aging. 2003;20(8):597-630. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200320080-00005. Drugs Aging. 2003. PMID: 12795627 Review.
-
A comparison of the efficacy and tolerability of brimonidine and latanoprost in adults with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension: a three-month, multicenter, randomized, double-masked, parallel-group trial.Clin Ther. 2001 Dec;23(12):1969-83. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(01)80150-8. Clin Ther. 2001. PMID: 11813932 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and side effects of latanoprost monotherapy compared to adding dorzolamide to timolol in patients with glaucoma and ocular hypertension--a three-month randomised study. Spanish Latanoprost Study Group.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2000 Jul-Sep;10(3):198-204. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2000. PMID: 11071026 Clinical Trial.
-
Three-month comparison of brimonidine and latanoprost as adjunctive therapy in glaucoma and ocular hypertension patients uncontrolled on beta-blockers: tolerance and peak intraocular pressure lowering.Ophthalmology. 2002 Feb;109(2):307-14; discussion 314-5. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(01)00936-8. Ophthalmology. 2002. PMID: 11825814 Clinical Trial.
-
Topical bimatoprost: a review of its use in open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension.Drugs Aging. 2002;19(3):231-48. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200219030-00008. Drugs Aging. 2002. PMID: 12027782 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical utility and differential effects of prostaglandin analogs in the management of raised intraocular pressure and ocular hypertension.Clin Ophthalmol. 2010 Jul 30;4:741-64. doi: 10.2147/opth.s10441. Clin Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 20689791 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of additional intraocular pressure reduction in patients changed to latanoprost/timolol fixed combination.BMC Ophthalmol. 2010 Mar 26;10:10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2415-10-10. BMC Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 20346127 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Latanoprost : an update of its use in glaucoma and ocular hypertension.Drugs Aging. 2003;20(8):597-630. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200320080-00005. Drugs Aging. 2003. PMID: 12795627 Review.
-
Latanoprost ophthalmic solution in the treatment of open angle glaucoma or raised intraocular pressure: a review.Clin Ophthalmol. 2008 Dec;2(4):897-905. Clin Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 19668444 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen and blood flow: players in the pathogenesis of glaucoma.Mol Vis. 2008 Jan 31;14:224-33. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 18334938 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Uusitalo RJ, Palkama A. Long-term evaluation of timolol. Acta Ophthalmol 1989;67:573–81. - PubMed
-
- Boger WP 3rd, Steinert RF, Puliafito CA, et al. Clinical trial comparing timolol ophthalmic solution to pilocarpine in open-angle glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 1978;86:8–18. - PubMed
-
- Hartenbaum D. The efficacy of dorzolamide, a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, in combination with timolol in the treatment of patients with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Clin Ther 1996;18:460–5. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman TJ, Canale P. Timolol—further observations. Ophthalmology 1979;86:166–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical