Corneal stromal changes following reconstruction by ex vivo expanded limbal epithelial cells in rabbits with total limbal stem cell deficiency
- PMID: 14660463
- PMCID: PMC1920578
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.87.12.1509
Corneal stromal changes following reconstruction by ex vivo expanded limbal epithelial cells in rabbits with total limbal stem cell deficiency
Abstract
Aim: To study corneal stromal changes and the presence of myofibroblasts after transplantation of ex vivo expanded limbal epithelium.
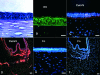
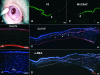
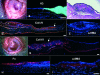
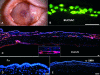
Methods: A state of limbal deficiency was induced in 16 rabbits. After transplantation with autologous ex vivo expanded limbal epithelium on amniotic membrane (AM), their clinical outcomes were classified as success, partial success or failure according to surface smoothness, stromal clarity, and vascularisation. Clinical outcomes were correlated with phenotypic outcomes of corneal, conjunctival, or mixed epithelium, defined by expression of K3 keratin or MUC5AC. Immunostaining was performed with antibodies against collagen IV, fibronectin, and alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) to assess stromal wound remodelling.
Results: Rabbits were sacrificed after a mean follow up of 10 (SD 3.3) months. Collagen IV, expressed in the basement membrane of all three groups, was found in the stroma of the partial success, but not in that of the success or the failure. Fibronectin was absent in the success and the failure, but expressed in the stroma of the partial success. Alpha-SMA was expressed in superficial stroma of the partial success, but suppressed in areas with AM remnants.
Conclusion: Restoration of a clear and transparent cornea is associated with a normal corneal epithelium and complete wound remodelling. In contrast, wound healing remains active and incomplete in conjunctivalised corneas, which remain opaque with myofibroblasts.
Figures
Comment in
-
Ocular surface reconstruction, amniotic membrane, and cultivated epithelial cells from the limbus.Br J Ophthalmol. 2003 Dec;87(12):1437-9. doi: 10.1136/bjo.87.12.1437-a. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003. PMID: 14660444 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tsai RJ F, Li L-M, Chen J- K. Reconstruction of damaged corneas by transplantation of autologous limbal epithelial cells. N Eng J Med 2000;343:86–93. - PubMed
-
- Schwab IR, Reyes M, Isseroff RR. Successful transplantation of bioengineered tissue replacements in patients with ocular surface disease. Cornea 2000;19:421–6. - PubMed
-
- Koizumi N, Inatomi T, Suzuki T, et al. Cultivated corneal epithelial transplantation for ocular surface reconstruction in acute phase of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol 2001;119:298–300. - PubMed
-
- Koizumi N, Inatomi T, Suzuki T, et al. Cultivated corneal epithelial stem cell transplantation in ocular surface disorders. Ophthalmology 2001;108:1569–74. - PubMed
-
- Grueterich M, Espana EM, Touhami A, et al. Phenotypic study of a case with successful transplantation of ex vivo expanded human limbal epithelium for unilateral total limbal stem cell deficiency. Ophthalmology 2002;109:1547–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
