Lipopolysaccharide 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (Kdo) core determines bacterial association of secreted toxins
- PMID: 14660669
- PMCID: PMC3525363
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M308633200
Lipopolysaccharide 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (Kdo) core determines bacterial association of secreted toxins
Abstract
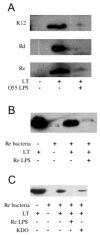
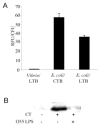
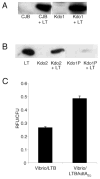
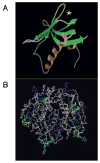
In contrast to cholera toxin (CT), which is secreted solubly by Vibrio cholerae across the outer membrane, heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) is retained on the surface of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) via an interaction with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We examined the nature of the association between LT and LPS. Soluble LT binds to the surface of LPS deep-rough biosynthesis mutants but not to lipid A, indicating that only the Kdo (3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonic acid) core is required for binding. Although capable of binding truncated LPS and Kdo, LT has a higher affinity for longer, more complete LPS species. A putative LPS binding pocket is proposed based on the crystal structure of the toxin. The ability to bind LPS and remain associated with the bacterial surface is not unique to LT, as CT also binds to E. coli LPS. However, neither LT nor CT is capable of binding to the surface of Vibrio. The core structures of Vibrio and E. coli LPS differ in that Vibrio contains a phosphorylated single Kdo-lipid A, and E. coli LPS contains unphosphorylated Kdo2-lipid A. We determined that the phosphate group on the Kdo core of Vibrio LPS prevents CT from binding, resulting in the secretion of soluble toxin. Because LT binds E. coli LPS, it remains associated with the extracellular bacterial surface and is released in association with outer membrane vesicles. We propose that difference in the extracellular fates of LT and CT contribute to the differences in disease caused by ETEC and Vibrio cholerae.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Residues of heat-labile enterotoxin involved in bacterial cell surface binding.J Bacteriol. 2009 May;191(9):2917-25. doi: 10.1128/JB.01622-08. Epub 2009 Mar 6. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19270095 Free PMC article.
-
A phosphoethanolamine transferase specific for the outer 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid residue of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Identification of the eptB gene and Ca2+ hypersensitivity of an eptB deletion mutant.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 3;280(22):21202-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500964200. Epub 2005 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15795227
-
Comparison of the carbohydrate-binding specificities of cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxins LTh-I, LT-IIa, and LT-IIb.Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1748-53. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1748-1753.1988. Infect Immun. 1988. PMID: 3290106 Free PMC article.
-
Structural biology and structure-based inhibitor design of cholera toxin and heat-labile enterotoxin.Int J Med Microbiol. 2004 Oct;294(4):217-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2004.07.002. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15532979 Review.
-
The sugar 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid (Kdo) as a characteristic component of bacterial endotoxin -- a review of its biosynthesis, function, and placement in the lipopolysaccharide core.Can J Microbiol. 2013 Oct;59(10):645-55. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2013-0490. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Can J Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24102217 Review.
Cited by
-
Using Vibrio natriegens for high-yield production of challenging expression targets and for protein deuteration.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 3:2023.11.03.565449. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.03.565449. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Biochemistry. 2024 Mar 5;63(5):587-598. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00612. PMID: 37961550 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Uptake of Helicobacter pylori outer membrane vesicles by gastric epithelial cells.Infect Immun. 2010 Dec;78(12):5054-61. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00299-10. Epub 2010 Sep 27. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20876296 Free PMC article.
-
Residues of heat-labile enterotoxin involved in bacterial cell surface binding.J Bacteriol. 2009 May;191(9):2917-25. doi: 10.1128/JB.01622-08. Epub 2009 Mar 6. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19270095 Free PMC article.
-
Fortifying the barrier: the impact of lipid A remodelling on bacterial pathogenesis.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Jul;11(7):467-81. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3047. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23748343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Offense and defense: microbial membrane vesicles play both ways.Res Microbiol. 2012 Nov-Dec;163(9-10):607-18. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2012.10.020. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Res Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23123555 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Merritt EA, Hol WG. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1995;5:165–171. - PubMed
-
- Sixma TK, Kalk KH, van Zanten BA, Dauter Z, Kingma J, Witholt B, Hol WG. J Mol Biol. 1993;230:890–918. - PubMed
-
- Mekalanos JJ, Swartz DJ, Pearson GD, Harford N, Groyne F, de Wilde M. Nature. 1983;306:551–557. - PubMed
-
- Dallas WS, Falkow S. Nature. 1980;288:499–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

