124I-labeled engineered anti-CEA minibodies and diabodies allow high-contrast, antigen-specific small-animal PET imaging of xenografts in athymic mice
- PMID: 14660722
- PMCID: PMC4167879
124I-labeled engineered anti-CEA minibodies and diabodies allow high-contrast, antigen-specific small-animal PET imaging of xenografts in athymic mice
Abstract
Prolonged clearance kinetics have hampered the development of intact antibodies as imaging agents, despite their ability to effectively deliver radionuclides to tumor targets in vivo. Genetically engineered antibody fragments display rapid, high-level tumor uptake coupled with rapid clearance from the circulation in the athymic mouse/LS174T xenograft model. The anticarcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) T84.66 minibody (single-chain Fv fragment [scFv]-C(H)3 dimer, 80 kDa) and T84.66 diabody (noncovalent dimer of scFv, 55 kDa) exhibit pharmacokinetics favorable for radioimmunoimaging. The present work evaluated the minibody or diabody labeled with (124)I, for imaging tumor-bearing mice using a high-resolution small-animal PET system.
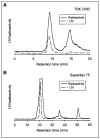
Methods: Labeling was conducted with 0.2-0.3 mg of protein and 65-98 MBq (1.7-2.6 mCi) of (124)I using an iodination reagent. Radiolabeling efficiencies ranged from 33% to 88%, and immunoreactivity was 42% (diabody) or >90% (minibody). In vivo distribution was evaluated in athymic mice bearing paired LS174T human colon carcinoma (CEA-positive) and C6 rat glioma (CEA-negative) xenografts. Mice were injected via the tail vein with 1.9-3.1 MBq (53-85 microCi) of (124)I-minibody or with 3.1 MBq (85 microCi) of (124)I-diabody and imaged at 4 and 18 h by PET. Some mice were also imaged using (18)F-FDG 2 d before imaging with (124)I-minibody.
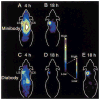
Results: PET images using (124)I-labeled minibody or diabody showed specific localization to the CEA-positive xenografts and relatively low activity elsewhere in the mice, particularly by 18 h. Target-to-background ratios for the LS174T tumors versus soft tissues using (124)I-minibody were 3.05 at 4 h and 11.03 at 18 h. Similar values were obtained for the (124)I-diabody (3.95 at 4 h and 10.93 at 18 h). These results were confirmed by direct counting of tissues after the final imaging. Marked reduction of normal tissue activity, especially in the abdominal region, resulted in high-contrast images at 18 h for the (124)I-anti-CEA diabody. CEA-positive tumors as small as 11 mg (<3 mm in diameter) could be imaged, and (124)I-anti-CEA minibodies, compared with (18)F-FDG, demonstrated highly specific localization.
Conclusion: (124)I labeling of engineered antibody fragments provides a promising new class of tumor-specific probes for PET imaging of tumors and metastases.
Figures
Comment in
-
Genetically engineered antibody fragments and PET imaging: a new era of radioimmunodiagnosis.J Nucl Med. 2003 Dec;44(12):1970-2. J Nucl Med. 2003. PMID: 14660723 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
PET imaging of colorectal cancer in xenograft-bearing mice by use of an 18F-labeled T84.66 anti-carcinoembryonic antigen diabody.J Nucl Med. 2007 Feb;48(2):304-10. J Nucl Med. 2007. PMID: 17268029
-
Genetically engineered antibody fragments and PET imaging: a new era of radioimmunodiagnosis.J Nucl Med. 2003 Dec;44(12):1970-2. J Nucl Med. 2003. PMID: 14660723 No abstract available.
-
Minibody: A novel engineered anti-carcinoembryonic antigen antibody fragment (single-chain Fv-CH3) which exhibits rapid, high-level targeting of xenografts.Cancer Res. 1996 Jul 1;56(13):3055-61. Cancer Res. 1996. PMID: 8674062
-
124I-Labeled anti-prostate stem cell antigen affinity-matured A11 minibody.2010 Jun 23 [updated 2010 Jul 19]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2010 Jun 23 [updated 2010 Jul 19]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20662135 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
64Cu-1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane-N,N',N'',N'''-tetraacetic acid-T84.66 scFv-human serum albumin.2008 Jul 2 [updated 2008 Sep 2]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2008 Jul 2 [updated 2008 Sep 2]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641733 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-carcinoembryonic antigen single-chain variable fragment antibody variants bind mouse and human neonatal Fc receptor with different affinities that reveal distinct cross-species differences in serum half-life.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 29;287(27):22927-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.355131. Epub 2012 May 8. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22570488 Free PMC article.
-
Radioimaging of light chain amyloid with a fibril-reactive monoclonal antibody.J Nucl Med. 2006 Dec;47(12):2016-24. J Nucl Med. 2006. PMID: 17138745 Free PMC article.
-
Iodine-124: a promising positron emitter for organic PET chemistry.Molecules. 2010 Apr 13;15(4):2686-718. doi: 10.3390/molecules15042686. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20428073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody Targeted PET Imaging of 64Cu-DOTA-Anti-CEA PEGylated Lipid Nanodiscs in CEA Positive Tumors.Bioconjug Chem. 2020 Mar 18;31(3):743-753. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00854. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Bioconjug Chem. 2020. PMID: 31961138 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction method for intrinsic random coincidence events from (176)Lu in low activity PET imaging.Radiol Phys Technol. 2014 Jul;7(2):235-45. doi: 10.1007/s12194-014-0258-1. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Radiol Phys Technol. 2014. PMID: 24496884
References
-
- Colcher D, Goel A, Pavlinkova G, Beresford G, Booth B, Batra SK. Effects of genetic engineering on the pharmacokinetics of antibodies. Q J Nucl Med. 1999;43:132–139. - PubMed
-
- Wu AM, Yazaki PJ. Designer genes: recombinant antibody fragments for biological imaging. Q J Nucl Med. 2000;44:268–283. - PubMed
-
- Huston JS, George AJ, Adams GP, et al. Single-chain Fv radioimmunotargeting. Q J Nucl Med. 1996;40:320–333. - PubMed
-
- Yokota T, Milenic DE, Whitlow M, Wood JF, Hubert SL, Schlom J. Microautoradiographic analysis of the normal organ distribution of radioiodinated single-chain Fv and other immunoglobulin forms. Cancer Res. 1993;53:3776–3783. - PubMed
-
- Hu S, Shively L, Raubitschek A, et al. Minibody: a novel engineered anti-carcinoembryonic antigen antibody fragment (single-chain Fv-CH3) which exhibits rapid, high-level targeting of xenografts. Cancer Res. 1996;56:3055–3061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
