Complement system on the attack in autoimmunity
- PMID: 14660739
- PMCID: PMC281650
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI20309
Complement system on the attack in autoimmunity
Abstract
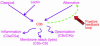
The antiphospholipid syndrome is characterized clinically by fetal loss and thrombosis and serologically by the presence of autoantibodies to lipid-binding proteins. In a model of this procoagulant condition in which these antibodies are injected into pregnant mice, fetal loss was prevented by blocking of complement activation. Specifically, interaction of complement component 5a (C5a) with its receptor is necessary for thrombosis of placental vasculature. Inhibition of complement activation may have a therapeutic role in this disease.
Figures
Comment on
-
Complement C5a receptors and neutrophils mediate fetal injury in the antiphospholipid syndrome.J Clin Invest. 2003 Dec;112(11):1644-54. doi: 10.1172/JCI18817. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 14660741 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Complement C5a receptors and neutrophils mediate fetal injury in the antiphospholipid syndrome.J Clin Invest. 2003 Dec;112(11):1644-54. doi: 10.1172/JCI18817. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 14660741 Free PMC article.
-
The role of complement in the antiphospholipid syndrome: a novel mechanism for pregnancy morbidity.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Aug;42(1):66-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2012.01.001. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22405029 Review.
-
Complement inhibition keeps mothers calm and avoids fetal rejection.Immunol Invest. 2008;37(5):645-59. doi: 10.1080/08820130802191615. Immunol Invest. 2008. PMID: 18716942 Review.
-
Guilty as charged: all available evidence implicates complement's role in fetal demise.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2008 Mar;59(3):183-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2007.00572.x. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18275511
-
Heparin prevents antiphospholipid antibody-induced fetal loss by inhibiting complement activation.Nat Med. 2004 Nov;10(11):1222-6. doi: 10.1038/nm1121. Epub 2004 Oct 17. Nat Med. 2004. PMID: 15489858
Cited by
-
Blockade of autoantibody-initiated tissue damage by using recombinant fab antibody fragments against pathogenic autoantigen.Am J Pathol. 2010 Feb;176(2):914-25. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090744. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20042683 Free PMC article.
-
C5a induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in brain vascular endothelial cells in experimental lupus.Immunology. 2016 Aug;148(4):407-19. doi: 10.1111/imm.12619. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Immunology. 2016. PMID: 27213693 Free PMC article.
-
Tracing the molecular pathogenesis of antiphospholipid syndrome.J Clin Invest. 2008 Oct;118(10):3276-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI37243. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18802489 Free PMC article.
-
Opposite Profiles of Complement in Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Among Patients With Antiphospholipid Antibodies (aPL).Front Immunol. 2019 May 7;10:885. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00885. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31134052 Free PMC article.
-
The quantitative role of alternative pathway amplification in classical pathway induced terminal complement activation.Clin Exp Immunol. 2004 Dec;138(3):439-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02627.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15544620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Silverstein, A.M. 1989. A history of immunology. Academic Press Inc. San Diego, California, USA. 422 pp.
-
- Matsumoto I, Staub A, Benoist C, Mathis D. Arthritis provoked by linked T and B cell recognition of a glycolytic enzyme. Science. 1999; 286:1732–1735. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto I, et al. How antibodies to a ubiquitous cytoplasmic enzyme may provoke joint-specific autoimmune disease. Nat. Immunol. 2002; 3:360–365. - PubMed
-
- Ji H, et al. Arthritis critically dependent on innate immune system players. Immunity. 2002; 16:157–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

