Typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a university hospital setting by using novel software for spa repeat determination and database management
- PMID: 14662923
- PMCID: PMC309029
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.12.5442-5448.2003
Typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a university hospital setting by using novel software for spa repeat determination and database management
Abstract
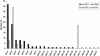
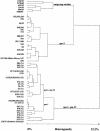
The spa gene of Staphylococcus aureus encodes protein A and is used for typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). We used sequence typing of the spa gene repeat region to study the epidemiology of MRSA at a German university hospital. One hundred seven and 84 strains were studied during two periods of 10 and 4 months, respectively. Repeats and spa types were determined by Ridom StaphType, a novel software tool allowing rapid repeat determination, data management and retrieval, and Internet-based assignment of new spa types following automatic quality control of DNA sequence chromatograms. Isolates representative of the most abundant spa types were subjected to multilocus sequence typing and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. One of two predominant spa types was replaced by a clonally related variant in the second study period. Ten unique spa types, which were equally distributed in both study periods, were recovered. The data show a rapid dynamics of clone circulation in a university hospital setting. spa typing was valuable for tracking of epidemic isolates. The data show that disproval of epidemiologically suggested transmissions of MRSA is one of the main objectives of spa typing in departments with a high incidence of MRSA.
Figures

References
-
- Claus, H., C. Cuny, B. Pasemann, and W. Witte. 1998. A database system for fragment patterns of genomic DNA of Staphylococcus aureus. Zentbl. Bakteriol. 287:105-116. - PubMed
-
- Cosgrove, S. E., G. Sakoulas, E. N. Perencevich, M. J. Schwaber, A. W. Karchmer, and Y. Carmeli. 2003. Comparison of mortality associated with methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 36:53-59. - PubMed
-
- Crisostomo, M. I., H. Westh, A. Tomasz, M. Chung, D. C. Oliveira, and H. de Lencastre. 2001. The evolution of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: similarity of genetic backgrounds in historically early methicillin-susceptible and -resistant isolates and contemporary epidemic clones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:9865-9870. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

