Dissection of Arabidopsis Bax inhibitor-1 suppressing Bax-, hydrogen peroxide-, and salicylic acid-induced cell death
- PMID: 14671021
- PMCID: PMC301392
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.014613
Dissection of Arabidopsis Bax inhibitor-1 suppressing Bax-, hydrogen peroxide-, and salicylic acid-induced cell death
Abstract
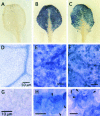
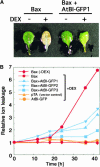
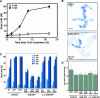
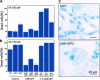
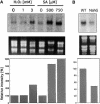
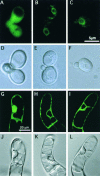
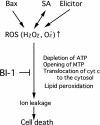
Overexpression of plant Bax Inhibitor-1 (BI-1) was able to suppress Bax-mediated cell death in yeast and Arabidopsis. Here, we demonstrate that reactive oxygen species production induced by the ectopic expression of Bax was insensitive to the coexpression of AtBI-1. Similarly, H2O2- or salicylic acid-mediated cell death also was suppressed in tobacco BY-2 cells overexpressing AtBI-1. To define the functional domain of AtBI-1 as a cell death suppressor, a truncated series of the AtBI-1 protein was analyzed in yeast possessing a galactose-inducible mammalian Bax. The results showed that DeltaC-AtBI-1 (with the C-terminal 14 amino acids deleted) lost the ability to sustain cell growth. Furthermore, a mutant protein in which the C-terminal seven amino acid residues of AtBI-1 were replaced with others lacking a coiled-coil structure failed to inhibit cell death, suggesting that the C-terminal region is essential for the inhibition of cell death. We also noted that the C-terminal hydrophilic region was interchangeable between animal and plant Bax inhibitors.
Figures

References
-
- An, G., Ebert, R.R., Mitra, A., and Ha, S.B. (1998). Binary vectors. In Plant Molecular Biology Manual, S.B. Gelvin and R.A. Schilperoort, eds (Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers), pp. 1–19.
-
- Bolduc, N., and Brisson, L.F. (2003). Antisense down regulation of NtBI-1 in tobacco BY-2 cells induces accelerated cell death upon carbon starvation. FEBS Lett. 532, 111–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

