Herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early gene expression is required for the induction of apoptosis in human epithelial HEp-2 cells
- PMID: 14671104
- PMCID: PMC303390
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.1.224-239.2004
Herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early gene expression is required for the induction of apoptosis in human epithelial HEp-2 cells
Abstract
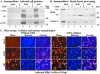
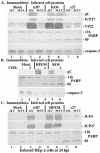
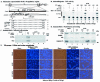
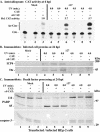
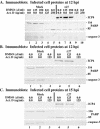
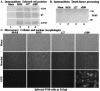
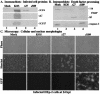
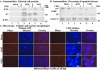
Wild-type herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) induces apoptosis in human epithelial HEp-2 cells, but infected cell proteins produced later in infection block the process from killing the cells. Thus, HSV-1 infection in the presence of the translational inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX) results in apoptosis. Our specific goal was to gain insight as to the viral feature(s) responsible for triggering apoptosis during HSV-1 infection. We now report the following. (i) No viral protein synthesis or death factor processing was detected after infection with HSV-1(HFEMtsB7) at 39.5 degrees C; this mutant virus does not inject its virion DNA into the nucleus at this nonpermissive temperature. (ii) No death factor processing or apoptotic morphological changes were detected following infection with UV-irradiated, replication-defective viruses possessing transcriptionally active incoming VP16. (iii) Addition of the transcriptional inhibitor actinomycin D prevented death factor processing upon infection with the apoptotic, ICP27-deletion virus HSV-1(vBSDelta27). (iv) Apoptotic morphologies and death factor processing were not observed following infection with HSV-1(d109), a green fluorescent protein-expressing recombinant virus possessing deletions of all five immediate-early (IE) (or alpha) genes. (v) Finally, complete death factor processing was observed upon infection with the VP16 transactivation domain-mutant HSV-1(V422) in the presence of CHX. Based on these findings, we conclude that (vi) the expression of HSV-1 alpha/IE genes is required for the viral induction of apoptosis and (vii) the transactivation activity of VP16 is not necessary for this induction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accumulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 early and leaky-late proteins correlates with apoptosis prevention in infected human HEp-2 cells.J Virol. 2001 Jan;75(2):1013-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.2.1013-1030.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11134315 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB is required for apoptosis prevention during herpes simplex virus type 1 infection.J Virol. 2003 Jul;77(13):7261-80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.13.7261-7280.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12805425 Free PMC article.
-
ICP0 gene expression is a herpes simplex virus type 1 apoptotic trigger.J Virol. 2006 Jul;80(14):6810-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00334-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16809287 Free PMC article.
-
[Visualization of viruses in living cells].Uirusu. 2008 Dec;58(2):117-24. doi: 10.2222/jsv.58.117. Uirusu. 2008. PMID: 19374190 Review. Japanese.
-
The herpes simplex virus type 1 infected cell protein 22.Virol Sin. 2010 Feb;25(1):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s12250-010-3080-x. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Virol Sin. 2010. PMID: 20960278 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Innate defense mechanisms against HSV-1 infection in the target tissues, skin and brain.J Neurovirol. 2016 Oct;22(5):641-649. doi: 10.1007/s13365-016-0440-9. Epub 2016 Apr 20. J Neurovirol. 2016. PMID: 27098517
-
Herpes simplex virus blocks apoptosis by precluding mitochondrial cytochrome c release independent of caspase activation in infected human epithelial cells.Apoptosis. 2007 Jan;12(1):19-35. doi: 10.1007/s10495-006-0330-3. Apoptosis. 2007. PMID: 17080326 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1)-induced apoptosis in human dendritic cells as a result of downregulation of cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein and reduced expression of HSV-1 antiapoptotic latency-associated transcript sequences.J Virol. 2010 Jan;84(2):1034-46. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01409-09. Epub 2009 Nov 11. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19906927 Free PMC article.
-
The virion host shut-off (vhs) protein blocks a TLR-independent pathway of herpes simplex virus type 1 recognition in human and mouse dendritic cells.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 18;5(2):e8684. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008684. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20174621 Free PMC article.
-
The chicken chorioallantoic membrane model for isolation of CRISPR/cas9-based HSV-1 mutant expressing tumor suppressor p53.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 20;18(10):e0286231. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286231. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37862369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aubert, M., and J. A. Blaho. 2001. Modulation of apoptosis during herpes simplex virus infection in human cells. Microbes Infect. 3:859-866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

