EBNA3C coactivation with EBNA2 requires a SUMO homology domain
- PMID: 14671118
- PMCID: PMC303384
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.1.367-377.2004
EBNA3C coactivation with EBNA2 requires a SUMO homology domain
Abstract
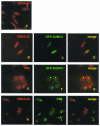
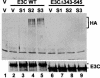
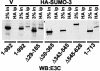
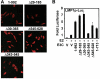
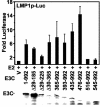
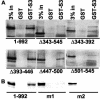
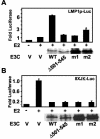
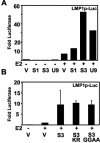
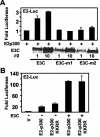
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 3C (EBNA3C) is critical for EBV immortalization of infected B lymphocytes and can coactivate the EBV LMP1 promoter with EBNA2. EBNA3C amino acids 365 to 545 are necessary and sufficient for coactivation and are required for SUMO-1 and SUMO-3 interaction. We found that EBNA3C but not EBNA3CDelta343-545 colocalized with SUMO-1 in nuclear bodies and was modified by SUMO-2, SUMO-3, and SUMO-1. EBNA3C amino acids 545 to 628 and amino acids 30 to 365 were also required for EBNA3C sumolation and nuclear body localization but were dispensable for coactivation, indicating that EBNA3C sumolation is not required for coactivation. Furthermore, EBNA3C amino acids 476 to 992 potently coactivated with EBNA2 but EBNA3C amino acids 516 to 922 lacked activity, indicating that amino acids 476 to 515 are critical for coactivation. EBNA3C amino acids 476 to 515 include DDDVIEV(507-513), which are similar to SUMO-1 EEDVIEV(84-90). EBNA3C m1 and m2 point mutations, DDD(507-509) mutated to AAA and DVIEVID(509-513) mutated to AVIAVIA, respectively, diminished SUMO-1 and SUMO-3 interaction in directed yeast two-hybrid and glutathione S-transferase pulldown assays. Furthermore, EBNA3C m1 and m2 did not coactivate the LMP1 promoter with EBNA2. Overexpression of wild-type SUMO-1, SUMO-3, and the SUMO-conjugating enzyme UBC9 coactivated the LMP1 promoter with EBNA2. Since EBNA2 activation is dependent on p300/CBP, the possible effect of EBNA3C on p300-mediated transcription was assayed. EBNA3C potentiated transcription of p300 fused to a heterologous DNA binding domain, whereas EBNA3C m1 and m2 did not. All of these data are consistent with a model in which EBNA3C upregulates EBNA2-mediated gene activation by binding to a sumolated repressor and inhibiting repressive effects on p300/CBP and other transcription factor(s) at EBNA2-regulated promoters.
Figures

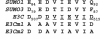
Similar articles
-
EBNA3C interacts with Gadd34 and counteracts the unfolded protein response.Virol J. 2009 Dec 29;6:231. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-6-231. Virol J. 2009. PMID: 20040105 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C putative repression domain mediates coactivation of the LMP1 promoter with EBNA-2.J Virol. 2002 Jan;76(1):232-42. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.1.232-242.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11739688 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 3 (EBNA3) Proteins Regulate EBNA2 Binding to Distinct RBPJ Genomic Sites.J Virol. 2015 Dec 30;90(6):2906-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02737-15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26719268 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein Barr nuclear antigen EBNA3C regulates transcription, cell transformation and cell migration.Front Biosci. 2002 Mar 1;7:d704-16. doi: 10.2741/subraman. Front Biosci. 2002. PMID: 11861219 Review.
-
SUMO and transcriptional regulation.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004 Apr;15(2):201-10. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2003.12.001. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15209380 Review.
Cited by
-
EBNA3C interacts with Gadd34 and counteracts the unfolded protein response.Virol J. 2009 Dec 29;6:231. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-6-231. Virol J. 2009. PMID: 20040105 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO junction-what's your function? New insights through SUMO-interacting motifs.EMBO Rep. 2007 Jun;8(6):550-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400980. EMBO Rep. 2007. PMID: 17545995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deregulation of the cell cycle machinery by Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C.Future Virol. 2009 Jan;4(1):79-91. doi: 10.2217/17460794.4.1.79. Future Virol. 2009. PMID: 25635182 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C facilitates G1-S transition by stabilizing and enhancing the function of cyclin D1.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Feb 10;7(2):e1001275. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001275. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21347341 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C augments Mdm2-mediated p53 ubiquitination and degradation by deubiquitinating Mdm2.J Virol. 2009 May;83(9):4652-69. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02408-08. Epub 2009 Feb 25. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19244339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allday, M. J., D. H. Crawford, and J. A. Thomas. 1993. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 6 induces expression of the EBV latent membrane protein and an activated phenotype in Raji cells. J. Gen. Virol. 74:361-369. - PubMed
-
- Allday, M. J., D. H. Crawford, and J. A. Thomas. 1993. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 6 induces expression of the EBV latent membrane protein and an activated phenotype in Raji cells. J. Gen. Virol. 74:361-369. - PubMed
-
- Arany, Z., D. Newsome, E. Oldread, D. M. Livingston, and R. Eckner. 1995. A family of transcriptional adaptor proteins targeted by the E1A oncoprotein. Nature 374:81-84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

