Hepatitis C virus subgenomic replicons in the human embryonic kidney 293 cell line
- PMID: 14671129
- PMCID: PMC303421
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.1.491-501.2004
Hepatitis C virus subgenomic replicons in the human embryonic kidney 293 cell line
Abstract
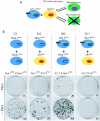
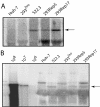
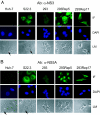
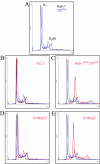
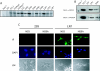
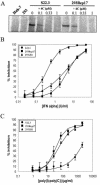
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infects liver cells and its replication in other cells is incompletely defined. Human hepatoma Huh-7 cells harboring subgenomic HCV replicons were used in somatic cell fusion experiments with human embryonic kidney 293 cells as a means of examining the permissiveness of 293 cells for HCV subgenomic RNA replication. 293 cells were generally not permissive for replication of Huh-7 cell-adapted replicons. However, upon coculturing of the two cell lines, we selected rare replicon-containing cells, termed 293Rep cells, that resembled parental 293 cells. Direct metabolic labeling of cells with (33)P in the presence of actinomycin D and Northern blotting to detect the negative strand of the replicon demonstrated functional RNA replicons in 293Rep cells. Furthermore, Western blots revealed that 293Rep cells expressed the HCV nonstructural proteins as well as markers of the naïve 293 cells but not Huh-7 cells. Propidium iodide staining and fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis of 293Rep cells revealed that clone 293Rep17 closely resembled naïve 293 cells. Transfection of total RNA from 293Rep17 into naïve 293 cells produced replicon-containing 293 cell lines with characteristics distinct from those of Huh-7-derived replicon cell lines. Relative to Huh-7 replicons, the 293 cell replicons were less sensitive to inhibition by alpha interferon and substantially more sensitive to inhibition by poly(I)-poly(C) double-stranded RNA. This study established HCV subgenomic replicons in nonhepatic 293 cells and demonstrated their utility in expanding the study of cellular HCV RNA replication.
Figures

References
-
- Alter, H. J., and L. B. Seeff. 2000. Recovery, persistence, and sequelae in hepatitis C virus infection: a perspective on long-term outcome. Semin. Liver Dis. 20:17-35. - PubMed
-
- Blight, K. J., A. A. Kolykhalov, and C. M. Rice. 2000. Efficient initiation of HCV RNA replication in cell culture. Science 290:1972-1974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

