Physiological levels of hydrocortisone maintain an optimal chondrocyte extracellular matrix metabolism
- PMID: 14672893
- PMCID: PMC1754735
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2002.005298
Physiological levels of hydrocortisone maintain an optimal chondrocyte extracellular matrix metabolism
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of physiological doses of hydrocortisone on synthesis and turnover of cell associated matrix (CAM) by human chondrocytes obtained from normal articular cartilage.
Methods: Human articular cartilage cells were obtained from visually intact cartilage of the femoral condyles of five donors and maintained in culture for one week to reach equilibrium in accumulated CAM compounds. 0, 0.05, 0.20, and 1.0 micro g/ml hydrocortisone was added to the nutrient media during the entire culture period. Cells were liberated and levels of CAM aggrecan, type II collagen, and fibronectin, of intracellular IGF-1, IL1alpha and beta, and of their respective plasma membrane bound receptors IGFR1, IL1RI, and the decoy receptor IL1RII, were assayed by flow cytometry.
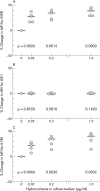
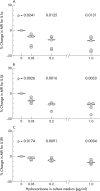
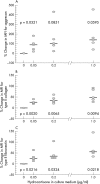
Results: In comparison with controls, hydrocortisone treated chondrocytes, at all concentrations, expressed significantly higher plasma membrane bound IGFR1. Intracellular IGF-1 levels remained unchanged. Together with these changes, reflecting an increased ability to synthesise extracellular matrix (ECM) macromolecules, hydrocortisone treated cells expressed significantly higher amounts of the plasma membrane bound decoy IL1RII. Concurrently, intracellular IL1alpha and beta levels and membrane bound IL1RI were down regulated. Levels of CAM aggrecan, type II collagen, and fibronectin were significantly up regulated in the chondrocytes treated with hydrocortisone.
Conclusion: 0.05 micro g/ml hydrocortisone treated chondrocytes had decreased catabolic signalling pathways and showed an enhanced ability to synthesise ECM macromolecules. Because IL1 activity was decreased and the expression of IL1RII decoy receptor enhanced, more of the ECM macromolecules produced remained accumulated in the CAM of the chondrocytes. The effects were obtained at doses comparable with physiological plasma levels of hydrocortisone in humans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cyclodextrin polysulphates repress IL-1 and promote the accumulation of chondrocyte extracellular matrix.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005 Oct;13(10):887-95. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2005.02.014. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005. PMID: 16202919
-
Homeostasis of the extracellular matrix of normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage chondrocytes in vitro.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003 Nov;11(11):801-9. doi: 10.1016/s1063-4584(03)00168-7. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003. PMID: 14609533
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1-induced interleukin-1 receptor II overrides the activity of interleukin-1 and controls the homeostasis of the extracellular matrix of cartilage.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 May;48(5):1281-91. doi: 10.1002/art.11061. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 12746901
-
[A new mechanism of action of chondroitin sulfates ACS4-ACS6 in osteoarthritic cartilage].Presse Med. 2002 Sep 14;31(29):1383-5. Presse Med. 2002. PMID: 12375394 Review. French.
-
Molecular roles in membrane receptor signaling pathways and cascade reactions in chondrocytes: a review.J Mol Histol. 2025 Feb 23;56(2):94. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10368-9. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 39988650 Review.
Cited by
-
Chondrotoxicity of Intra-Articular Injection Treatment: A Scoping Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 26;25(13):7010. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137010. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000119 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of various factors on articular cartilage and their implications on arthroscopic procedures: A review of literature.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020 May;11(Suppl 3):S396-S401. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2019.06.017. Epub 2019 Jun 20. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020. PMID: 32523300 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Extracellular matrix production in vitro in cartilage tissue engineering.J Transl Med. 2014 Apr 5;12:88. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-88. J Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 24708713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Intra-articular Corticosteroids on Articular Cartilage: A Systematic Review.Orthop J Sports Med. 2015 Apr 27;3(5):2325967115581163. doi: 10.1177/2325967115581163. eCollection 2015 May. Orthop J Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 26674652 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

