The kinesin KIF17b and RNA-binding protein TB-RBP transport specific cAMP-responsive element modulator-regulated mRNAs in male germ cells
- PMID: 14673085
- PMCID: PMC307608
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2536695100
The kinesin KIF17b and RNA-binding protein TB-RBP transport specific cAMP-responsive element modulator-regulated mRNAs in male germ cells
Abstract
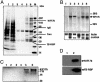
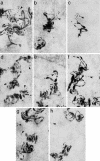
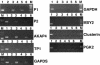
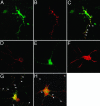
Testis brain RNA-binding protein (TB-RBP), the mouse orthologue of the human protein Translin, is a widely expressed and highly conserved protein with proposed functions in chromosomal translocations, mitotic cell division, and mRNA transport, stabilization, and storage. Targeted inactivation of TB-RBP leads to abnormalities in fertility and behavior. A testis-enriched kinesin KIF17b coimmunoprecipitates with TB-RBP in a RNA-protein complex containing specific cAMP-responsive element modulator (CREM)-regulated mRNAs. The specificity of this interaction is confirmed by in vivo RNA-protein crosslinking and transfections of hippocampal neurons. Combining in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry at the electron microscope level, a temporally sequential dissociation of KIF17b and TB-RBP from specific mRNAs is detected with TB-RBP release coincident with the time of mRNA translation, indicating a separation of the processes of transport and translation. We conclude that KIF17b serves as a molecular motor component of a TB-RBP-mouse ribonucleoprotein complex transporting a group of specific CREM-regulated mRNAs in mammalian male postmeiotic germ cells. Because KIF17b has been reported to control CREM-dependent transcription in male germ cells by regulating the intracellular location of the transcriptional coactivator activator of CREM in testis, this indicates that one kinesin links the processes of transcription and transport of specific mRNAs in mammalian male germ cells.
Figures
References
-
- Braun, R. E., Behringer, R. R., Peschon, J. J., Brinster, R. L. & Palmiter, R. D. (1989) Nature 337, 373–376. - PubMed
-
- Zou, Y., Millette, C. F. & Sperry, A. O. (2002) Biol. Reprod. 66, 843–855. - PubMed
-
- Aoki, K., Suzuki, K., Sugano, T., Tasaka, T., Nakahara, K., Kuge, O., Omori, A. & Kasai, M. (1995) Nat. Genet. 10, 167–174. - PubMed
-
- Morales, C. R., Lefrancois, S., Chennathukuzhi, V., El-Alfy, M., Wu, X., Yang, J., Gerton, G. L. & Hecht, N. B. (2002) Dev. Biol. 246, 480–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

