Repair kinetics of genomic interstrand DNA cross-links: evidence for DNA double-strand break-dependent activation of the Fanconi anemia/BRCA pathway
- PMID: 14673148
- PMCID: PMC303365
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.1.123-134.2004
Repair kinetics of genomic interstrand DNA cross-links: evidence for DNA double-strand break-dependent activation of the Fanconi anemia/BRCA pathway
Abstract
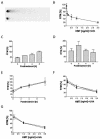
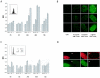
The detailed mechanisms of DNA interstrand cross-link (ICL) repair and the involvement of the Fanconi anemia (FA)/BRCA pathway in this process are not known. Present models suggest that recognition and repair of ICL in human cells occur primarily during the S phase. Here we provide evidence for a refined model in which ICLs are recognized and are rapidly incised by ERCC1/XPF independent of DNA replication. However, the incised ICLs are then processed further and DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) form exclusively in the S phase. FA cells are fully proficient in the sensing and incision of ICL as well as in the subsequent formation of DSB, suggesting a role of the FA/BRCA pathway downstream in ICL repair. In fact, activation of FANCD2 occurs slowly after ICL treatment and correlates with the appearance of DSB in the S phase. In contrast, activation is rapid after ionizing radiation, indicating that the FA/BRCA pathway is specifically activated upon DSB formation. Furthermore, the formation of FANCD2 foci is restricted to a subpopulation of cells, which can be labeled by bromodeoxyuridine incorporation. We therefore conclude that the FA/BRCA pathway, while being dispensable for the early events in ICL repair, is activated in S-phase cells after DSB have formed.
Figures
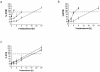
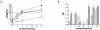
Similar articles
-
XPF-ERCC1 participates in the Fanconi anemia pathway of cross-link repair.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;29(24):6427-37. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00086-09. Epub 2009 Oct 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19805513 Free PMC article.
-
Double-strand breaks induce homologous recombinational repair of interstrand cross-links via cooperation of MSH2, ERCC1-XPF, REV3, and the Fanconi anemia pathway.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 Nov;6(11):1670-8. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.06.002. Epub 2007 Jul 31. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 17669695 Free PMC article.
-
A Boolean network model of the FA/BRCA pathway.Bioinformatics. 2012 Mar 15;28(6):858-66. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts036. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22267503
-
Regulation of DNA cross-link repair by the Fanconi anemia/BRCA pathway.Genes Dev. 2012 Jul 1;26(13):1393-408. doi: 10.1101/gad.195248.112. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22751496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The FANC/BRCA Pathway Releases Replication Blockades by Eliminating DNA Interstrand Cross-Links.Genes (Basel). 2020 May 25;11(5):585. doi: 10.3390/genes11050585. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32466131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ATR couples FANCD2 monoubiquitination to the DNA-damage response.Genes Dev. 2004 Aug 15;18(16):1958-63. doi: 10.1101/gad.1196104. Genes Dev. 2004. PMID: 15314022 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and regulation of incisions during DNA interstrand cross-link repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2014 Jul;19:135-42. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.03.018. Epub 2014 Apr 24. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014. PMID: 24768452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Standards for Quantitative Measurement of DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 12;24(6):5427. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065427. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginsenosides synergize with mitomycin C in combating human non-small cell lung cancer by repressing Rad51-mediated DNA repair.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Mar;39(3):449-458. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.53. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 28836581 Free PMC article.
-
The Fanconi anemia core complex is required for efficient point mutagenesis and Rev1 foci assembly.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 Jun 1;7(6):902-11. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.03.001. Epub 2008 Apr 29. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 18448394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akkari, Y. M., R. L. Bateman, C. A. Reifsteck, A. D. D'Andrea, S. B. Olson, and M. Grompe. 2001. The 4N cell cycle delay in Fanconi anemia reflects growth arrest in late S phase. Mol. Genet. Metab. 74:403-412. - PubMed
-
- Bessho, T. 2003. Induction of DNA replication-mediated double strand breaks by psoralen DNA interstrand cross-links. J. Biol. Chem. 278:5250-5254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
