Sex differences in the alterations of Na(+), K(+)-ATPase following ischaemia-reperfusion injury in the rat kidney
- PMID: 14673189
- PMCID: PMC1664838
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.054825
Sex differences in the alterations of Na(+), K(+)-ATPase following ischaemia-reperfusion injury in the rat kidney
Abstract
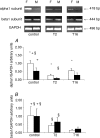
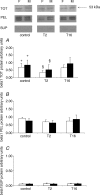
Postischaemic acute renal failure (ARF) is influenced by sex. Na(+), K(+)-ATPase (NKA) plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of postischaemic ARF. We tested the impact of sex on mRNA, protein expression, cellular distribution and enzyme activity of NKA following renal ischaemia-reperfusion (I-R) injury. The left renal pedicle of uninephrectomized female (F) and male (M) Wistar rats was clamped for 55 min followed by 2 h (T2) and 16 h (T16) of reperfusion. Uninephrectomized, sham-operated F and M rats served as controls (n= 6 per group). Blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine and renal histology were evaluated to detect the severity of postischaemic ARF. mRNA expression of NKA alpha1 and beta1 subunits were detected by RT-PCR. The effect of I-R on cellular distribution was compared by Triton X-100 extraction. Cellular proteins were divided into Triton-insoluble and Triton-soluble fractions and assessed by Western blot. NKA enzyme activity was also determined. After the ischaemic insult blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine were higher and renal histology showed more rapid progression in M versus F (P < 0.05). mRNA expression of the NKA alpha1 subunit decreased in I-R groups versus controls, but was higher in F versus M both in control and I-R groups (P < 0.05). However, protein levels of the NKA alpha1 subunit in total tissue homogenate did not differ in controls, but were higher in F versus M in I-R groups (P < 0.05). Triton X-100 extractability was lower in F versus M at T16 (P < 0.05). NKA enzyme activity was the same in controls, but was higher in F versus M in I-R groups (T2: 14.9 +/- 2.3 versus 9.15 +/- 2.21 U) (T16: 11.7 +/- 4.1 versus 5.65 +/- 2.3 U; P < 0.05). mRNA and protein expression of the NKA beta1 subunit did not differ between F and M in any of the protocol. We concluded that NKA is more protected from the detrimental effects of postischaemic injury in females. Higher mRNA and protein expression of the NKA alpha1 subunit and higher enzyme activity might be additional contributing factors to the improved postischaemic renal function of female rats.
Figures



References
-
- Alejandro VS, Nelson WJ, Huie P, Sibley RK, Dafoe D, Kuo P, Scandling JD, Jr, Myers BD. Postischemic injury, delayed function and Na+/K+-ATPase distribution in the transplanted kidney. Kidney Int. 1995;48:1308–1315. - PubMed
-
- Aufricht C, Bidmon B, Ruffingshofer D, Regele H, Herkner K, Siegel NJ, Kashgarian M, Van Why S. Ischemic conditioning prevents Na,K-ATPase dissociation from the cytoskeletal cellular fraction after repeat renal ischemia in rats. Pediatr Res. 2002;51:722–727. - PubMed
-
- Bertorello AM, Ridge KM, Chibalin AV, Katz AI, Sznajder JI. Isoproterenol increases Na+-K+-ATPase activity by membrane insertion of alpha-subunits in lung alveolar cells. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:L20–L27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

