Knockout of ERK5 causes multiple defects in placental and embryonic development
- PMID: 14675480
- PMCID: PMC324396
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-3-11
Knockout of ERK5 causes multiple defects in placental and embryonic development
Abstract
Background: ERK5 is a member of the mitogen activated protein kinase family activated by certain mitogenic or stressful stimuli in cells, but whose physiological role is largely unclear.
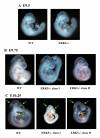
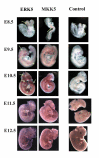
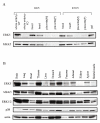
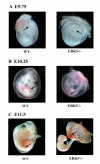
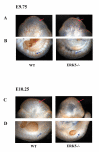
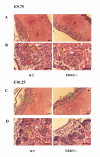
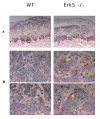
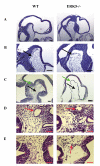
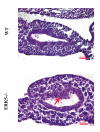
Results: To help determine the function of ERK5 we have used gene targeting to inactivate this gene in mice. Here we report that ERK5 knockout mice die at approximately E10.5. In situ hybridisation for ERK5, and its upstream activator MKK5, showed strong expression in the head and trunk of the embryo at this stage of development. Between E9.5 and E10.5, multiple developmental problems are seen in the ERK5-/- embryos, including an increase in apoptosis in the cephalic mesenchyme tissue, abnormalities in the hind gut, as well as problems in vascular remodelling, cardiac development and placental defects.
Conclusion: Erk5 is essential for early embryonic development, and is required for normal development of the vascular system and cell survival.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Erk5 null mice display multiple extraembryonic vascular and embryonic cardiovascular defects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jul 9;99(14):9248-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.142293999. Epub 2002 Jul 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12093914 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of MAP kinases: insights from gene-targeting studies.J Biochem. 2004 Jun;135(6):653-6. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvh078. J Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15213239 Review.
-
Essential role of p38alpha MAP kinase in placental but not embryonic cardiovascular development.Mol Cell. 2000 Jul;6(1):109-16. Mol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10949032
-
[Gene expression of extracellular-signal regulated protein kinase 5 and their MAPKK in fetal skin hypertrophic scars].Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2004 May;20(3):222-4. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15449628 Chinese.
-
Regulation of cellular functions by the ERK5 signalling pathway.Cell Signal. 2006 Jun;18(6):753-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.11.003. Epub 2006 Jan 6. Cell Signal. 2006. PMID: 16376520 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic analysis of bisphenol AF on early growth and development of zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae.Environ Sci Ecotechnol. 2020 Aug 5;4:100054. doi: 10.1016/j.ese.2020.100054. eCollection 2020 Oct. Environ Sci Ecotechnol. 2020. PMID: 36157705 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and characterization of an iminocoumarin scaffold as an inhibitor of MEKK2 (MAP3K2).Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jan 29;496(1):205-211. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.027. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29309787 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide induces cytokine production and decreases extravillous trophoblast invasion through a mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated pathway: possible mechanisms of first trimester placental dysfunction.Hum Reprod. 2012 Jan;27(1):61-72. doi: 10.1093/humrep/der362. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Hum Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22052387 Free PMC article.
-
MEK5 and ERK5 are mediators of the pro-myogenic actions of IGF-2.J Cell Sci. 2009 Sep 1;122(Pt 17):3104-12. doi: 10.1242/jcs.045757. Epub 2009 Aug 4. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19654213 Free PMC article.
-
Nutraceuticals as Modulators of Molecular Placental Pathways: Their Potential to Prevent and Support the Treatment of Preeclampsia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 13;25(22):12167. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212167. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596234 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

