Changes in local S4 environment provide a voltage-sensing mechanism for mammalian hyperpolarization-activated HCN channels
- PMID: 14676285
- PMCID: PMC2217414
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200308918
Changes in local S4 environment provide a voltage-sensing mechanism for mammalian hyperpolarization-activated HCN channels
Abstract
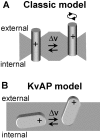
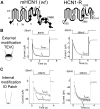
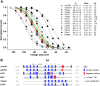
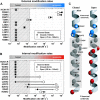
The positively charged S4 transmembrane segment of voltage-gated channels is thought to function as the voltage sensor by moving charge through the membrane electric field in response to depolarization. Here we studied S4 movements in the mammalian HCN pacemaker channels. Unlike most voltage-gated channel family members that are activated by depolarization, HCN channels are activated by hyperpolarization. We determined the reactivity of the charged sulfhydryl-modifying reagent, MTSET, with substituted cysteine (Cys) residues along the HCN1 S4 segment. Using an HCN1 channel engineered to be MTS resistant except for the chosen S4 Cys substitution, we determined the reactivity of 12 S4 residues to external or internal MTSET application in either the closed or open state of the channel. Cys substitutions in the NH2-terminal half of S4 only reacted with external MTSET; the rates of reactivity were rapid, regardless of whether the channel was open or closed. In contrast, Cys substitutions in the COOH-terminal half of S4 selectively reacted with internal MTSET when the channel was open. In the open state, the boundary between externally and internally accessible residues was remarkably narrow (approximately 3 residues). This suggests that S4 lies in a water-filled gating canal with a very narrow barrier between the external and internal solutions, similar to depolarization-gated channels. However, the pattern of reactivity is incompatible with either classical gating models, which postulate a large translational or rotational movement of S4 within a gating canal, or with a recent model in which S4 forms a peripheral voltage-sensing paddle (with S3b) that moves within the lipid bilayer (the KvAP model). Rather, we suggest that voltage sensing is due to a rearrangement in transmembrane segments surrounding S4, leading to a collapse of an internal gating canal upon channel closure that alters the shape of the membrane field around a relatively static S4 segment.
Figures

Comment in
-
How S4 segments move charge. Let me count the ways.J Gen Physiol. 2004 Jan;123(1):1-4. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200308975. Epub 2003 Dec 15. J Gen Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14676286 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aggarwal, S.K., and R. MacKinnon. 1996. Contribution of the S4 segment to gating charge in the Shaker K+ channel. Neuron. 16:1169–1177. - PubMed
-
- Akabas, M.H., D.A Stauffer, M. Xu, and A. Karlin. 1992. Acetylcholine receptor channel structure probed in cysteine-substitution mutants. Science. 258:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Baker, O.S., H.P. Larsson, L.M. Mannuzzu, and E.Y. Isacoff. 1998. Three transmembrane conformations and sequence-dependent displacement of the S4 domain in shaker K+ channel gating. Neuron. 20:1283–1294. - PubMed
-
- Bezanilla, F. 2000. The voltage sensor in voltage-dependent ion channels. Physiol. Rev. 80:555–592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

