TempliPhi: A sequencing template preparation procedure that eliminates overnight cultures and DNA purification
- PMID: 14676313
- PMCID: PMC2279908
TempliPhi: A sequencing template preparation procedure that eliminates overnight cultures and DNA purification
Abstract
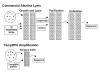
Preparing plasmid templates for DNA sequencing is the most time-consuming step in the sequencing process. Current template preparation methods rely on a labor-intensive, multistep procedure that takes up to 24 h and produces templates of varying quality and quantity. The TempliPhi DNA Sequencing Template Amplification Kit eliminates the requirement for extended bacterial growth prior to sequencing and saves laboratory personnel hands-on time by eliminating the centrifugation and transfer steps currently required by older preparatory methods. In addition, costly purification filters and columns are not necessary, as amplified product can be added directly to a sequencing reaction. Starting material can be any circular template from a colony, culture, glycerol stock, or plaque. Based on rolling circle amplification and employing bacteriophage Phi29 DNA polymerase, the method can produce 3-5 microg of template directly from a single bacterial colony in as little as 4 h. Implementation of these procedures in a laboratory or core sequencing facility can decrease cost on tips, plates, and other plasticware, while at the same time increase throughput.
Figures


References
-
- Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989: 1.21–1.39.
-
- Botstein D, Waddell CH, King J. Mechanism of head assembly and DNA encapsulation in Salmonella Phage P22. J Mol Biol 1973;80:669–695. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
