Antitumor efficacy of cytotoxic drugs and the monoclonal antibody 806 is enhanced by the EGF receptor inhibitor AG1478
- PMID: 14676326
- PMCID: PMC307660
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2036503100
Antitumor efficacy of cytotoxic drugs and the monoclonal antibody 806 is enhanced by the EGF receptor inhibitor AG1478
Abstract
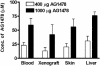
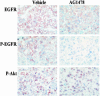
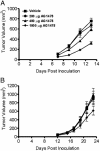
Blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling with specific inhibitors of the EGFR tyrosine kinase retards cellular proliferation and arrests the growth of tumor xenografts. AG1478, an inhibitor of the EGFR tyrosine kinase, is used in laboratory studies; however, its therapeutic potential has not been elucidated. Therefore, we evaluated an aqueous form of AG1478 for its antitumor activity in mice bearing human xenografts expressing the WT EGFR or a naturally occurring ligand-independent truncation of the EGFR [delta2-7 (de2-7) EGFR or EGFRvIII]. Parenteral administration of soluble AG1478 blocked phosphorylation of the EGFR at the tumor site and inhibited the growth of A431 xenografts that overexpress the WT EGFR and glioma xenografts expressing the de2-7 EGFR. Strikingly, even subtherapeutic doses of AG1478 significantly enhanced the efficacy of cytotoxic drugs, with the combination of AG1478 and temozolomide displaying synergistic antitumor activity against human glioma xenografts. AG1478 was also examined in combination with mAb 806, an anti-EGFR antibody that was raised against the de2-7 EGFR but unexpectedly also binds a subset of the EGFR expressed in cells exhibiting amplification of the EGFR gene. The combination of AG1478 and mAb 806 displayed additive, and in some cases synergistic, antitumor activity against tumor xenografts overexpressing the EGFR. Here, we demonstrate that different classes of inhibitors to the EGFR can have synergistic antitumor activity in vivo. These results establish the antitumor efficacy of the EGFR inhibitor AG1478 and provide a rationale for its clinical evaluation in combination with both chemotherapy and other EGFR therapeutics.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Treatment of human tumor xenografts with monoclonal antibody 806 in combination with a prototypical epidermal growth factor receptor-specific antibody generates enhanced antitumor activity.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Sep 1;11(17):6390-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2653. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16144944
-
Human glioblastoma xenografts overexpressing a tumor-specific mutant epidermal growth factor receptor sensitized to cisplatin by the AG1478 tyrosine kinase inhibitor.J Neurosurg. 2001 Sep;95(3):472-9. doi: 10.3171/jns.2001.95.3.0472. J Neurosurg. 2001. PMID: 11565870
-
Monoclonal antibody 806 inhibits the growth of tumor xenografts expressing either the de2-7 or amplified epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) but not wild-type EGFR.Cancer Res. 2001 Jul 15;61(14):5355-61. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11454674
-
Drug combinations enhancing the antineoplastic effects of erlotinib in high-grade glioma.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2011 Sep;6(3):384-94. doi: 10.2174/157489211796957748. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21612575 Review.
-
Aberrant receptor signaling in human malignant gliomas: mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Cancer Lett. 2001 Jan;162 Suppl:S17-S21. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(00)00648-0. Cancer Lett. 2001. PMID: 11164186 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Novel Therapeutic Opportunities for Glioblastoma Using Patient-Derived Cell Cultures.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 2;15(5):1562. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051562. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900355 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in Combination with Temozolomide against Tumor Angiogenesis in a Glioblastoma Model.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 8;13(19):5029. doi: 10.3390/cancers13195029. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638512 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR inhibitor enhances cisplatin sensitivity of human glioma cells.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011 Dec;31(6):773-778. doi: 10.1007/s11596-011-0675-x. Epub 2011 Dec 16. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 22173497
-
Antibodies specifically targeting a locally misfolded region of tumor associated EGFR.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Mar 31;106(13):5082-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811559106. Epub 2009 Mar 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19289842 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors in Glioblastoma: Current Status and Future Possibilities.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 15;25(4):2316. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042316. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396993 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mendelsohn, J. (2002) J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 1S-13S. - PubMed
-
- Arteaga, C. L. (2002) Semin. Oncol. 29, 3-9. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson, R. I., Gee, J. M. & Harper, M. E. (2001) Eur. J. Cancer 37, Suppl. 4, S9-S15. - PubMed
-
- de Bono, J. S. & Rowinsky, E. K. (2002) Trends Mol. Med. 8, S19-S26. - PubMed
-
- Herbst, R. S. & Shin, D. M. (2002) Cancer 94, 1593-1611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

