Phase I clinical trial of the bispecific antibody MDX-H210 (anti-FcgammaRI x anti-HER-2/neu) in combination with Filgrastim (G-CSF) for treatment of advanced breast cancer
- PMID: 14676800
- PMCID: PMC2395280
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601367
Phase I clinical trial of the bispecific antibody MDX-H210 (anti-FcgammaRI x anti-HER-2/neu) in combination with Filgrastim (G-CSF) for treatment of advanced breast cancer
Abstract
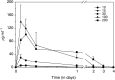
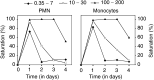
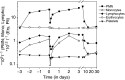
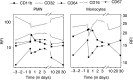
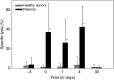
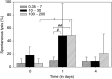
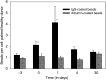
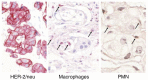
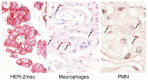
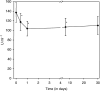
A phase I study of the bispecific antibody MDX-H210 in combination with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) was performed in stage IV breast carcinoma patients, overexpressing HER-2/neu. MDX-H210, constructed by crosslinking antigen binding fragments (F(ab') fragments) of monoclonal antibody (mAb) H22 to Fc gamma receptor I (FcgammaRI), and mAb 520C9 to HER-2/neu, respectively, mediates the lysis of tumour cells in vitro, and in human FcgammaRI transgenic mouse models. The proto-oncogene HER-2/neu is overexpressed in approximately 30% of breast cancer patients, and represents a promising target for antibody-based immunotherapy. Fc gamma receptor I (CD64) is an effective trigger molecule, which is expressed on monocytes/macrophages, immature dendritic cells, and G-CSF-primed polymorphonuclear cells (PMN). Patients received G-CSF (Filgrastim) for 8 consecutive days, and cohorts of three patients were treated on day 4 with escalating, single doses of MDX-H210. A total of 30 patients were included, and treatment was generally well tolerated, without reaching dose-limiting toxicity. Side effects consisted mainly of fever and short periods of chills, which were timely related to elevated plasma levels of interleukin 6 and tumour necrosis factor alpha. In the last two cohorts, MDX-H210 plasma levels exceeded 1 microg ml(-1), and on circulating myeloid cells >50% saturation of FcgammaRI was found until day 4. These effector cells were highly effective in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Immunohistochemical analyses of tumour biopsies in individual patients documented infiltration of monocytes and PMN after MDX-H210 infusion. Although the clinical course of the disease was not altered by the single dose of MDX-H210, a favourable toxicity profile--even at high doses--and remarkable biological effects were seen when combined with G-CSF. Therefore, the combination of G-CSF and MDX-H210 should be evaluated in further immunotherapeutical strategies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
G-CSF-stimulated PMN in immunotherapy of breast cancer with a bispecific antibody to Fc gamma RI and to HER-2/neu (MDX-210).J Hematother. 1995 Oct;4(5):415-21. doi: 10.1089/scd.1.1995.4.415. J Hematother. 1995. PMID: 8581378 Review.
-
Bispecific antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of HER2/neu-overexpressing tumor cells by Fc gamma receptor type I-expressing effector cells.Cancer Res. 1997 Sep 15;57(18):4008-14. Cancer Res. 1997. PMID: 9307286
-
Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships of the bispecific antibody MDX-H210 when administered in combination with interferon gamma: a multiple-dose phase-I study in patients with advanced cancer which overexpresses HER-2/neu.J Immunol Methods. 2001 Feb 1;248(1-2):149-65. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(00)00355-0. J Immunol Methods. 2001. PMID: 11223076 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I study of a HER2/neu bispecific antibody with granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor in patients with metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2/neu.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1999 Apr;48(1):9-21. doi: 10.1007/s002620050543. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1999. PMID: 10235484 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical experience with CD64-directed immunotherapy. An overview.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1997 Nov-Dec;45(3-4):210-5. doi: 10.1007/s002620050435. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1997. PMID: 9435876 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retargeting T cells for HER2-positive tumor killing by a bispecific Fv-Fc antibody.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 23;8(9):e75589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075589. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24086580 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting nucleotide metabolism: a promising approach to enhance cancer immunotherapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Apr 27;15(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01263-x. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35477416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Bs20x22 anti-CD20-CD22 bispecific antibody has more lymphomacidal activity than do the parent antibodies alone.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011 Jun;60(6):771-80. doi: 10.1007/s00262-011-0978-6. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011. PMID: 21347809 Free PMC article.
-
Testing for HER2 in Breast Cancer: A Continuing Evolution.Patholog Res Int. 2010 Dec 6;2011:903202. doi: 10.4061/2011/903202. Patholog Res Int. 2010. PMID: 21188214 Free PMC article.
-
Bridging the gap with multispecific immune cell engagers in cancer and infectious diseases.Cell Mol Immunol. 2024 Jul;21(7):643-661. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01176-4. Epub 2024 May 24. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38789528 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams GP, Schier R, McCall AM, Simmons HH, Horak EM, Alpaugh RK, Marks JD, Weiner LM (2001) High affinity restricts the localization and tumor penetration of single-chain fv antibody molecules. Cancer Res 61: 4750–4755 - PubMed
-
- Baselga J (2001) Clinical trials of Herceptin (trastuzumab). Eur J Cancer 37(Suppl. 1): S18–S24 - PubMed
-
- Becker W, Fischbach W, Reiners C, Borner W (1986) Three-phase white blood cell scan: diagnostic validity in abdominal inflammatory diseases. J Nucl Med 27: 1109–1115 - PubMed
-
- Brittenden J, Heys SD, Ross J, Eremin O (1996) Natural killer cells and cancer. Cancer 77: 1226–1243 - PubMed
-
- Clynes RA, Towers TL, Presta LG, Ravetch JV (2000) Inhibitory Fc receptors modulate in vivo cytotoxicity against tumor targets. Nat Med 6: 443–446 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

