Immature anti-inflammatory response in neonates
- PMID: 14678274
- PMCID: PMC1808915
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02313.x
Immature anti-inflammatory response in neonates
Abstract
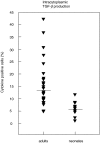
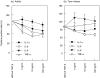
The inflammatory response plays a major role in the induction of several neonatal diseases. We hypothesize that an imbalance between the pro- and anti-inflammatory response is crucial for the previously shown enhanced production of proinflammatory cytokines in term and preterm infants during infection. To test this hypothesis, we compared the capacity to produce the main anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and TGF-beta in term infants, preterm infants and adults at different levels of synthesis by quantitative real time reverse-transcribed PCR, flow cytometry, as well as enzyme-linked immunoassay. Term and preterm infants showed a profoundly diminished IL-10 mRNA-expression and IL-10 production after stimulation. In addition, the amount of TGF-beta-positive lymphocytes was significantly less in neonates than adults. Furthermore, there was a considerably lower inhibition of production of IL-1alpha, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-alpha by the use of recombinant IL-10 in term and preterm infants compared with adults. These results demonstrate not only a diminished anti-inflammatory capacity but also a reduced response to anti-inflammatory stimuli in term and preterm infants. From these data we conclude that neonates display an immature compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome (CARS) which may predispose preterm infants to harmful effects of proinflammatory cytokines resulting in severe organ sequelae during infection.
Figures


References
-
- Bagchi A, Viscardi RM, Taciak V, Ensor JE, McCrea KA, Hasday JD. Increased activity of interleukin-6 but not tumor necrosis factor-a in lung lavage of premature infants is associated with the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Res. 1994;36:244–52. - PubMed
-
- Jones CA, Cayabyab RG, Kwong KYC, Stotts C, Wong B, Hamdan H, Minoo P, DeLemos RA. Undetectable interleukin (IL)-10 and persistent IL-8 expression early in hyaline membrane disease: a possible developmental basis for the predisposition to chronic lung inflammation in preterm newborns. Pediatr Res. 1996;39:966–75. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yoon BH, Romero R, Yang SH, Jun JK, Kim IO, Choi JH, Syn HC. Interleukin-6 concentrations in umbilical cord plasma are elevated in neonates with white matter lesions associated with periventricular leukomalacia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996;174:1433–40. - PubMed
-
- Kilpatrick L, Harris MC. Cytokines and the inflammatory response. In: Polin RA, Fox WW, editors. Fetal and Neonatal Physiology. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 1997. pp. 1967–78.
-
- Pillay V, Savage N, Laburn H. Circulating cytokine concentrations and cytokine production by monocytes from newborn babies and adults. Pflugers Arch. 1994;428:197–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

