The arginine-16 beta2-adrenoceptor polymorphism predisposes to bronchoprotective subsensitivity in patients treated with formoterol and salmeterol
- PMID: 14678342
- PMCID: PMC1884417
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01955.x
The arginine-16 beta2-adrenoceptor polymorphism predisposes to bronchoprotective subsensitivity in patients treated with formoterol and salmeterol
Abstract
Aims: The relationship between beta2-adrenoceptor polymorphisms and bronchoprotective response with long-acting beta2-adrenoceptor agonists is unknown.
Methods: We retrospectively analysed data from six placebo-controlled randomized studies in corticosteroid treated asthmatics where formoterol or salmeterol were administered over a 1-2-week period, with prior 1-2 week washout, assessing the primary end point of methacholine PD20 and adenosine monophosphate PC20, following first and last dose, expressed as doubling dose difference from placebo.
Results: There was no significant heterogeneity between the different studies. Patients who had homozygous or heterozygous genotypes containing the arginine-16 polymorphism (Arg16-Arg16 or Arg16-Gly16) had greater bronchoprotective subsensitivity compared with the homozygous glycine-16 genotype (Gly16-Gly16), amounting to a mean doubling dose difference of 1.49 (95% CI 0.50, 2.48), after the last dose. Subsensitivity of response was greater with formoterol than salmeterol after the last dose in all genotypes, especially with the arginine-16 polymorphism, amounting to a doubling dose difference of 3.00 (95% CI 1.01, 4.99) between formoterol and salmeterol.
Conclusions: Our retrospective analysis showed that the arginine-16 polymorphism was associated with subsensitivity of response for bronchoprotection, which was greater for formoterol than salmeterol. A prospective study will be required in order to further evaluate these findings, particularly to assess whether these differences are mirrored by exacerbations.
Figures
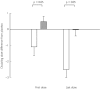
 ), compared with the Gly16-Gly16 genotype (
), compared with the Gly16-Gly16 genotype ( ).
).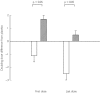
 ) and salmeterol (
) and salmeterol ( ), with SEM. A positive value indicates an increase whereas a negative value indicates a decrease in protection for either formoterol or salmeterol, relative to placebo. There was no significant difference between the formoterol and salmeterol for the degree of protection loss between first and last doses.
), with SEM. A positive value indicates an increase whereas a negative value indicates a decrease in protection for either formoterol or salmeterol, relative to placebo. There was no significant difference between the formoterol and salmeterol for the degree of protection loss between first and last doses.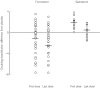
References
-
- Lipworth B, Tan S, Devlin M, et al. Effects of treatment with formoterol on bronchoprotection against methacholine. Am J Med. 1998;104:431–438. - PubMed
-
- Green SA, Cole G, Jacinto M, et al. A polymorphism of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor within the fourth transmembrane domain alters ligand binding and functional properties of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:23116–23121. - PubMed
-
- Green SA, Turki J, Bejarano P, et al. Influence of beta 2-adrenergic receptor genotypes on signal transduction in human airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995;13:25–33. - PubMed
-
- Tan S, Hall IP, Dewar J, et al. Association between beta 2-adrenoceptor polymorphism and susceptibility to bronchodilator desensitisation in moderately severe stable asthmatics. Lancet. 1997;350:995–999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

