Comparative genomic analysis as a tool for biological discovery
- PMID: 14678488
- PMCID: PMC1664741
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.050948
Comparative genomic analysis as a tool for biological discovery
Abstract
The recent completion of the human genome sequence has enabled the identification of a large fraction of our gene catalogue and their physical chromosomal position. However, current efforts lag at defining the cis-regulatory sequences that control the spatial and temporal patterns of each gene's expression. This task remains difficult due to our lack of knowledge of the vocabulary controlling gene regulation and the vast genomic search space, with greater than 95% of our genome being noncoding. Recent comparative genomic-based strategies are beginning to aid in the identification of functional sequences based on their high levels of evolutionary conservation. This has proven successful for comparisons between closely related species such as human-primate or human-mouse, but also holds true for distant evolutionary comparisons, such as human-fish or human-bird. In this review we provide support for the utility of cross-species sequence comparisons by illustrating several applications of this strategy, including the identification of new genes and functional non-coding sequences. We also discuss emerging concepts as this field matures, such as how to properly select which species for comparison, which may differ significantly between independent studies.
Figures

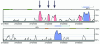
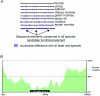
References
-
- Abrahams BS, Mak GM, Berry ML, Palmquist DL, Saionz JR, Tay A, Tan YH, Brenner S, Simpson EM, Venkatesh B. Novel vertebrate genes and putative regulatory elements identified at kidney disease and NR2E1/fierce loci. Genomics. 2002;80:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio S, Chapman J, Stupka E, Putnam N, Chia JM, Dehal P, Christoffels A, Rash S, Hoon S, Smit A, et al. Whole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Fugu rubripes. Science. 2002;297:1301–1310. - PubMed
-
- Bagheri-Fam S, Ferraz C, Demaille J, Scherer G, Pfeifer D. Comparative genomics of the SOX9 region in human and Fugu rubripes: conservation of short regulatory sequence elements within large intergenic regions. Genomics. 2001;78:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Shushan E, Marshak S, Shoshkes M, Cerasi E, Melloul D. A pancreatic beta-cell-specific enhancer in the human PDX-1 gene is regulated by hepatocyte nuclear factor 3beta (HNF-3beta), HNF-1alpha, and SPs transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:17533–17540. - PubMed
-
- Boffelli D, Mcauliffe J, Ovcharenko D, Lewis KD, Ovcharenko I, Pachter L, Rubin EM. Phylogenetic shadowing of primate sequences to find functional regions of the human genome. Science. 2003;299:1391–1394. - PubMed

