Calmodulin kinase is functionally targeted to the action potential plateau for regulation of L-type Ca2+ current in rabbit cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 14678498
- PMCID: PMC1664743
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.053314
Calmodulin kinase is functionally targeted to the action potential plateau for regulation of L-type Ca2+ current in rabbit cardiomyocytes
Abstract
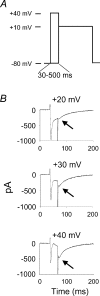
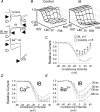
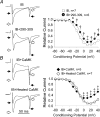
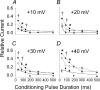
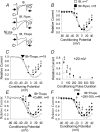
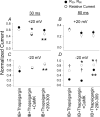
L-type Ca2+ current (ICa-L) triggers Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) and both SR and ICa-L are potential sources of intracellular Ca2+ (Ca2+i) for feedback regulation of ICa-L. Ca2+i bound to calmodulin (Ca2+-CaM) can inhibit ICa-L, while Ca2+-CaM can also activate Ca2+-CaM-dependent protein kinase II (CaMK) to increase ICa. However, it is not known whether ICa-L or the SR is the primary source of Ca2+ for ICa-L regulation. The L-type Ca2+ channel C terminus is implicated as a critical transduction element for ICa-L responses to Ca2+-CaM and CaMK, and the C terminus undergoes voltage-dependent steric changes, suggesting that Ca2+i control of ICa-L may also be regulated by cell membrane potential. We developed conditions to separately test the relationship of Ca2+-CaM and CaMK to ICa-L and SR Ca2+i release during voltage clamp conditions modelled upon time and voltage domains relevant to the cardiac action potential. Here we show that CaMK increases ICa-L after brief positive conditioning pulses, whereas Ca2+-CaM reduces ICa-L over a broad range of positive and negative conditioning potentials. SR Ca2+ release was required for both Ca2+-CaM and CaMK ICa-L responses after strongly positive conditioning pulses (+10 and +40 mV), while Ca2+i from ICa-L was sufficient for Ca2+-CaM during weaker depolarizations. These findings show that ICa-L responses to CaMK are voltage dependent and suggest a new model of L-type Ca2+ channel regulation where voltage-dependent changes control ICa-L responses to Ca2+-CaM and CaMK signalling.
Figures


References
-
- Balke CW, Wier WG. Ryanodine does not affect calcium current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes in which Ca2+ is buffered. Circ Res. 1991;68:897–902. - PubMed
-
- Balshaw DM, Xu L, Yamaguchi N, Pasek DA, Meissner G. Calmodulin binding and inhibition of cardiac muscle calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) J Biol Chem. 2001;276:20144–20153. - PubMed
-
- Bartel S, Vetter D, Schlegel WP, Wallukat G, Krause EG, Karczewski P. Phosphorylation of phospholamban at threonine-17 in the absence and presence of beta-adrenergic stimulation in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2000;32:2173–2185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

