Obesity-induced inflammatory changes in adipose tissue
- PMID: 14679172
- PMCID: PMC297006
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI20514
Obesity-induced inflammatory changes in adipose tissue
Abstract
Obesity is associated with a state of chronic, low-grade inflammation. Two manuscripts in this issue of the JCI (see the related articles beginning on pages 1796 and 1821) now report that obese adipose tissue is characterized by macrophage infiltration and that these macrophages are an important source of inflammation in this tissue. These studies prompt consideration of new models to include a major role for macrophages in the molecular changes that occur in adipose tissue in obesity.
Figures
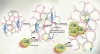
Comment on
-
Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue.J Clin Invest. 2003 Dec;112(12):1796-808. doi: 10.1172/JCI19246. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 14679176 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance.J Clin Invest. 2003 Dec;112(12):1821-30. doi: 10.1172/JCI19451. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 14679177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hotamisligil, G.S. 2003. Inflammation, TNFα and insulin resistance. In Diabetes mellitus. D. LeRoith, S.I. Taylor, and J.M. Olefsky, editors. Lippincott-Raven Publishers. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA. In press.
-
- Hirosumi J, et al. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature. 2002;420:333–336. - PubMed
-
- Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-α: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993;259:87–90. - PubMed
-
- Rosen BS, et al. Adipsin and complement factor D activity: an immune-related defect in obesity. Science. 1989;244:1483–1487. - PubMed
-
- Charriere G, et al. Preadipocyte conversion to macrophage. Evidence of plasticity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:9850–9855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

