Nurr1-RXR heterodimers mediate RXR ligand-induced signaling in neuronal cells
- PMID: 14681209
- PMCID: PMC305256
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.276003
Nurr1-RXR heterodimers mediate RXR ligand-induced signaling in neuronal cells
Abstract
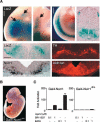
The retinoid X receptor (RXR) is essential as a common heterodimerization partner of several nuclear receptors (NRs). However, its function as a bona fide receptor for endogenous ligands has remained poorly understood. Such a role would depend on the existence of RXR activating ligands in vivo and on the ability of such ligands to influence relevant biological functions. Here we demonstrate the presence of endogenous RXR ligands in the embryonic central nervous system (CNS) and show that they can activate heterodimers formed between RXR and the orphan NR Nurr1 in vivo. Moreover, RXR ligands increase the number of surviving dopaminergic cells and other neurons in a process mediated by Nurr1-RXR heterodimers. These results provide evidence for a role of Nurr1 as a ligand-independent partner of RXR in its function as a bona fide ligand-activated NR. Finally, our findings identify RXR-Nurr1 heterodimers as a potential target in the treatment of neurodegenerative disease.
Figures






References
-
- Aarnisalo P., Kim, C.H., Lee, J.W., and Perlmann, T. 2002. Defining requirements for heterodimerization between the retinoid X receptor and the orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 35118-35123. - PubMed
-
- Aranda A. and Pascual, A. 2001. Nuclear hormone receptors and gene expression. Physiol. Rev. 81: 1269-1304. - PubMed
-
- Baker R.R. and Chang, H.Y. 1992. The hydrolysis of natural phosphatidylethanolamines by phospholipase A2 from rat serum: A degree of selectivity is shown for docosahexaenoate release. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1125: 56-61. - PubMed
-
- Baker K.D., Shewchuk, L.M., Kozlova, T., Makishima, M., Hassell, A., Wisely, B., Caravella, J.A., Lambert, M.H., Reinking, J.L., Krause, H., et al. 2003. The Drosophila orphan nuclear receptor DHR38 mediates an atypical ecdysteroid signaling pathway. Cell 113: 731-742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
