The KNOTTIN website and database: a new information system dedicated to the knottin scaffold
- PMID: 14681383
- PMCID: PMC308750
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh015
The KNOTTIN website and database: a new information system dedicated to the knottin scaffold
Abstract
The KNOTTIN website and database organize information about knottins or inhibitor cystine knots, small disulfide-rich proteins with a knotted topology. Thanks to their small size and high stability, knottins provide appealing scaffolds for protein engineering and drug design. Static pages present the main historical and recent results about knottin discoveries, sequences, structures, folding, functions, applications and bibliography. Database searches provide dynamically generated tabular reports or sequence alignments for knottin three-dimensional structures or sequences. BLAST/HMM searches are also available. A simple nomenclature, based on loop lengths between cysteines, is proposed and is complemented by a uniform numbering scheme. This standardization is applied to all knottin structures in the database, facilitating comparisons. Renumbered and structurally fitted knottin PDB files are available for download. The standardized numbering is used for automatic drawing of two-dimensional Colliers de Perles. The KNOTTIN website and database are available at http://knottin.cbs.cnrs.fr and http://knottin.com.
Figures
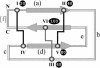


References
-
- Rees D.C. and Lipscomb,W.N. (1982) Refined crystal structure of the potato inhibitor complex of carboxypeptidase A at 2.5 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol., 160, 475–498. - PubMed
-
- Bode W., Greyling,H.J., Huber,R., Otlewski,J. and Wilusz,T. (1989) The refined 2.0 Å X-ray crystal structure of the complex formed between bovine β-trypsin and CMTI-I, a trypsin inhibitor from squash seeds (Cucurbita maxima). Topological similarity of the squash seed inhibitors with the carboxypeptidase A inhibitor from potatoes. FEBS Lett., 242, 285–292. - PubMed
-
- Chiche L., Gaboriaud,C., Heitz,A., Mornon,J.P., Castro,B. and Kollman,P.A. (1989) Use of restrained molecular dynamics in water to determine three-dimensional protein structure: prediction of the three-dimensional structure of Ecballium elaterium trypsin inhibitor II. Proteins, 6, 405–417. - PubMed
-
- Heitz A., Chiche,L., Le-Nguyen,D. and Castro,B. (1989) 1H 2D NMR and distance geometry study of the folding of Ecballium elaterium trypsin inhibitor, a member of the squash inhibitors family. Biochemistry, 28, 2392–2398. - PubMed
-
- Davis J.H., Bradley,E.K., Miljanich,G.P., Nadasdi,L., Ramachandran,J. and Basus,V.J. (1993) Solution structure of ω-conotoxin GVIA using 2-D NMR spectroscopy and relaxation matrix analysis. Biochemistry, 32, 7396–7405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

