WormBase: a multi-species resource for nematode biology and genomics
- PMID: 14681445
- PMCID: PMC308800
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh066
WormBase: a multi-species resource for nematode biology and genomics
Abstract
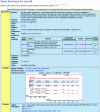
WormBase (http://www.wormbase.org/) is the central data repository for information about Caenorhabditis elegans and related nematodes. As a model organism database, WormBase extends beyond the genomic sequence, integrating experimental results with extensively annotated views of the genome. The WormBase Consortium continues to expand the biological scope and utility of WormBase with the inclusion of large-scale genomic analyses, through active data and literature curation, through new analysis and visualization tools, and through refinement of the user interface. Over the past year, the nearly complete genomic sequence and comparative analyses of the closely related species Caenorhabditis briggsae have been integrated into WormBase, including gene predictions, ortholog assignments and a new synteny viewer to display the relationships between the two species. Extensive site-wide refinement of the user interface now provides quick access to the most frequently accessed resources and a consistent browsing experience across the site. Unified single-page views now provide complete summaries of commonly accessed entries like genes. These advances continue to increase the utility of WormBase for C.elegans researchers, as well as for those researchers exploring problems in functional and comparative genomics in the context of a powerful genetic system.
Figures


References
-
- Riddle D.L., Blumenthal,T., Meyer,B.J. and Priess,J.R. (1997) C. elegans II. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY. - PubMed
-
- The C. elegans Sequencing Consortium (1998) Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: a platform for investigating biology. Science, 282, 2012–2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

