LIFEdb: a database for functional genomics experiments integrating information from external sources, and serving as a sample tracking system
- PMID: 14681468
- PMCID: PMC314201
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh022
LIFEdb: a database for functional genomics experiments integrating information from external sources, and serving as a sample tracking system
Abstract
We have implemented LIFEdb (http://www.dkfz.de/LIFEdb) to link information regarding novel human full-length cDNAs generated and sequenced by the German cDNA Consortium with functional information on the encoded proteins produced in functional genomics and proteomics approaches. The database also serves as a sample-tracking system to manage the process from cDNA to experimental read-out and data interpretation. A web interface enables the scientific community to explore and visualize features of the annotated cDNAs and ORFs combined with experimental results, and thus helps to unravel new features of proteins with as yet unknown functions.
Figures
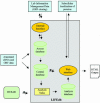

References
-
- Lander E.S., Linton,L.M., Birren,B., Nusbaum,C., Zody,M.C., Baldwin,J., Devon,K., Dewar,K., Doyle,M., FitzHugh,W. et al. (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Nature, 409, 860–921. - PubMed
-
- Venter J.C., Adams,M.D., Myers,E.W., Li,P.W., Mural,R.J., Sutton,G.G., Smith,H.O., Yandell,M., Evans,C.A., Holt,R.A. et al. (2001) The sequence of the human genome. Science, 291, 1304–1351. - PubMed
-
- Nagase T., Nakayama,M., Nakajima,D., Kikuno,R. and Ohara,O. (2001) Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XX. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro. DNA Res., 8, 85–95. - PubMed

