Concurrent infection with Schistosoma mansoni attenuates inflammation induced changes in colonic morphology, cytokine levels, and smooth muscle contractility of trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid induced colitis in rats
- PMID: 14684583
- PMCID: PMC1773910
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.53.1.99
Concurrent infection with Schistosoma mansoni attenuates inflammation induced changes in colonic morphology, cytokine levels, and smooth muscle contractility of trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid induced colitis in rats
Abstract
Background and aims: Crohn's disease, characterised by chronic T helper 1 (Th1) inflammation and dysmotility of the gut, is most prevalent in developed countries. Parasitic infections are most prevalent in developing countries and induce a T helper 2 (Th2) immune response. We hypothesised that this Th2 immune response protects against Th1 gut inflammation.
Methods: The parasite Schistosoma mansoni induces a transient Th2 immune response in the semipermissive rat host. 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid (TNBS) induced colitis is an experimental model of Th1-like gut inflammation. The effect of concurrent infection with S mansoni on the course of TNBS induced colitis was assessed using macroscopic and microscopic damage scores, histology, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity assay, cytokine production assay, and by studying in vitro contractility of longitudinal and circular colonic muscle strips.
Results: TNBS induced colitis that spontaneously healed after four weeks. Concurrent infection with S mansoni significantly reduced the duration of TNBS induced colitis to two weeks, as shown by macroscopic and microscopic damage scores and by a faster decrease in colonic MPO activity. TNBS increased colonic interleukin 2 (IL-2) production whereas S mansoni increased splenic IL-4 and IL-2 levels. Contractility of longitudinal and circular muscle strips was maximally inhibited one week after TNBS and normalised after three weeks. After four weeks, longitudinal muscle strip contractility was significantly increased. Concurrent infection with S mansoni normalised longitudinal muscle contractility after one week whereas circular muscle contractility remained inhibited.
Conclusions: Concurrent infection with S mansoni significantly attenuates TNBS induced colitis in the rat. Inflammation induced disturbances in contractility of longitudinal and circular colonic muscle strips may outlast the inflammatory reaction.
Figures




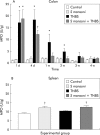
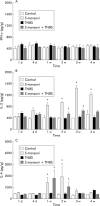
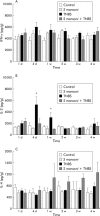
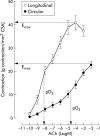
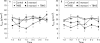
Comment in
-
Helminths and harmony.Gut. 2004 Jan;53(1):7-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.53.1.7. Gut. 2004. PMID: 14684567 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic potential of helminth soluble proteins in TNBS-induced colitis in mice.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009 Apr;15(4):491-500. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20787. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009. PMID: 19023900
-
Mycophenolate Mofetil Modulates Differentiation of Th1/Th2 and the Secretion of Cytokines in an Active Crohn's Disease Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 6;16(11):26654-66. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125985. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26561804 Free PMC article.
-
Role of nitric oxide in the impairment of circular muscle contractility of distended, uninflamed mid-colon in TNBS-induced acute distal colitis in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Sep 28;11(36):5677-84. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i36.5677. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16237764 Free PMC article.
-
Schistosoma mansoni infection modulates the immune response against allergic and auto-immune diseases.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2004;99(5 Suppl 1):27-32. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762004000900005. Epub 2004 Oct 13. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2004. PMID: 15486631 Review.
-
Preclinical Study in Vivo for New Pharmacological Approaches in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review of Chronic Model of TNBS-Induced Colitis.J Clin Med. 2019 Oct 1;8(10):1574. doi: 10.3390/jcm8101574. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31581545 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Concurrent infection with an intestinal helminth parasite impairs host resistance to enteric Citrobacter rodentium and enhances Citrobacter-induced colitis in mice.Infect Immun. 2005 Sep;73(9):5468-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.9.5468-5481.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16113263 Free PMC article.
-
Extracts of the rat tapeworm, Hymenolepis diminuta, suppress macrophage activation in vitro and alleviate chemically induced colitis in mice.Infect Immun. 2010 Mar;78(3):1364-75. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01349-08. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20028812 Free PMC article.
-
Acute distal colitis impairs gastric emptying in rats via an extrinsic neuronal reflex pathway involving the pelvic nerve.Gut. 2007 Feb;56(2):195-202. doi: 10.1136/gut.2006.104745. Epub 2006 Sep 14. Gut. 2007. PMID: 16973715 Free PMC article.
-
Larval Echinococcus multilocularis infection reduces dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis in mice by attenuating T helper type 1/type 17-mediated immune reactions.Immunology. 2018 May;154(1):76-88. doi: 10.1111/imm.12860. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Immunology. 2018. PMID: 29121394 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal prescription Chang'an II repairs intestinal mucosal barrier in rats with post-inflammation irritable bowel syndrome.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Jun;36(6):708-15. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.170. Epub 2015 May 11. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015. PMID: 25960135 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calkins BM, Mendeloff AI. Epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease. Epidemiol Rev 1986;8:60–91. - PubMed
-
- Hutt MSR. Epidemiology of chronic intestinal disease in Middle Africa. Isr J Med Sci 1979;15:314–17. - PubMed
-
- Mayberry J, Mann R. Inflammatory bowel disease in rural Sub-Saharan Africa: rarity of diagnosis in patients attending mission hospitals. Digestion 1989;44:172–6. - PubMed
-
- Rolon PA. Gastrointestinal pathology in South America. Isr J Med Sci 1979;15:318–21. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Major parasitic infections: a global review. World Health Stat Q 1986;39:145–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
