fMRI of the conscious rabbit during unilateral classical eyeblink conditioning reveals bilateral cerebellar activation
- PMID: 14684877
- PMCID: PMC6740957
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-37-11753.2003
fMRI of the conscious rabbit during unilateral classical eyeblink conditioning reveals bilateral cerebellar activation
Abstract
The relative contributions of the ipsilateral and contralateral cerebellar cortex and deep nuclei to delay eyeblink conditioning have been debated and are difficult to survey entirely using typical electrophysiological and lesion techniques. To address these issues, we used single-event functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in the conscious rabbit to visualize the entire cerebellum simultaneously during eyeblink conditioning sessions. Examination of the blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) response to a visual conditioning stimulus early in training revealed significant bilateral learning-related increases in the BOLD response in the anterior interpositus nucleus (IPA) and significant bilateral deactivation in hemispheric lobule VI (HVI) of the cerebellar cortex. Later in training, the BOLD response remained bilateral in the cortex and predominantly ipsilateral in the IPA. Conditioning stimulus-alone trials after conditioning revealed that both sides of HVI were affected similarly but that only the ipsilateral interpositus nucleus was activated. These results suggest that both sides of HVI normally influence the side of the IPA being conditioned and illustrate how fMRI can be used to examine multiple brain regions simultaneously in an awake, behaving animal to discover more rapidly the neural substrates of learning and memory.
Figures
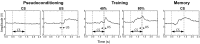
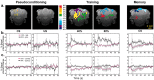
References
-
- Berthier NE, Moore JW ( 1986) Cerebellar Purkinje cell activity related to the classically conditioned nictitating membrane response. Exp Brain Res 63: 341-350. - PubMed
-
- Berthier NE, Moore JW ( 1990) Activity of deep cerebellar nuclear cells during classical conditioning of nictitating membrane extension in rabbits. Exp Brain Res 83: 44-54. - PubMed
-
- Chen N-K, Wyrwicz AM ( 2001) An optimized distortion correction technique for echo planar imaging. Magn Reson Med 45: 525-528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
