Perioperative recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (Filgrastim) treatment prevents immunoinflammatory dysfunction associated with major surgery
- PMID: 14685103
- PMCID: PMC1356195
- DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000103062.21049.82
Perioperative recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (Filgrastim) treatment prevents immunoinflammatory dysfunction associated with major surgery
Abstract
Objective: To examine the effects of perioperative rhG-CSF administration on immune function in patients subjected to major surgery.
Summary background data: Severe trauma, such as major surgery, initiates acute immunodysfunction which predisposes the patient towards infectious complications.
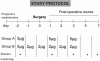
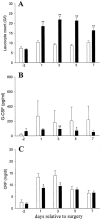
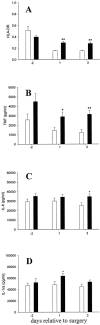
Methods: Sixty patients undergoing elective surgery received either recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor/rh G-CSF (Filgrastim) or a placebo perioperatively. At several time points before and after the surgical intervention immunofunctional parameters were assessed. RESULTS Leukocyte counts and serum levels of anti-inflammatory mediators (IL-1ra and TNF-R) were increased in Filgrastim-treated patients, while the post-operative acute phase response was attenuated. Monocyte deactivation (reduced TNF-alpha release and HLA-DR expression) and lymphocyte anergy (impaired mitogenic proliferation and reduced TH1 lymphokine release) were blunted and the incidence and severity of infectious complications were reduced.
Conclusions: These results suggest that Filgrastim treatment reinforces innate immunity, enabling better prevention of infection. Thus, this unique combination of hematopoietic, anti-inflammatory and anti-infectious effects on the innate immune system warrants further study of clinical efficacy and sepsis prophylaxis.
Figures
References
-
- Green DR, Faist E. Trauma and the immune response. Immunol Today. 1988;9:253–255. - PubMed
-
- Faist E, Schinkel C, Zimmer S. Update on the mechanisms of immune suppression of injury and immune modulation. World J Surg. 1996;20:454–459. - PubMed
-
- Schinkel C, Licht K, Zedler S, et al. Interferon-gamma modifies cytokine release in vitro by monocytes from surgical patients. J Trauma. 2001;50:321–327. - PubMed
-
- Volk HD, Reinke P, Falck P, et al. Diagnostic value of an immune monitoring program for the clinical management of immunosuppressed patients with septic complications. Clin Transplant. 1989;3:246–252.
-
- Faist E, Schinkel C, Zimmer S, et al. Inadequate interleukin-2 synthesis and interleukin-2 messenger expression following thermal and mechanical trauma in humans is caused by defective transmembrane signalling. J Trauma. 1993;34:846–853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

