A prospective randomized multi-center study for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with the X STOP interspinous implant: 1-year results
- PMID: 14685830
- PMCID: PMC3468027
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-003-0581-4
A prospective randomized multi-center study for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with the X STOP interspinous implant: 1-year results
Abstract
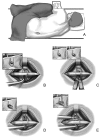
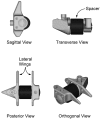
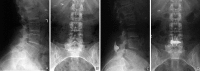
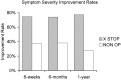
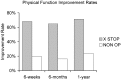
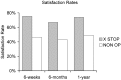
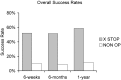
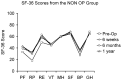
Patients suffering from neurogenic intermittent claudication secondary to lumbar spinal stenosis have historically been limited to a choice between a decompressive laminectomy with or without fusion or a regimen of non-operative therapies. The X STOP Interspinous Process Distraction System (St. Francis Medical Technologies, Concord, Calif.), a new interspinous implant for patients whose symptoms are exacerbated in extension and relieved in flexion, has been available in Europe since June 2002. This study reports the results from a prospective, randomized trial of the X STOP conducted at nine centers in the U.S. Two hundred patients were enrolled in the study and 191 were treated; 100 received the X STOP and 91 received non-operative therapy (NON OP) as a control. The Zurich Claudication Questionnaire (ZCQ) was the primary outcomes measurement. Validated for lumbar spinal stenosis patients, the ZCQ measures physical function, symptom severity, and patient satisfaction. Patients completed the ZCQ upon enrollment and at follow-up periods of 6 weeks, 6 months, and 1 year. Using the ZCQ criteria, at 6 weeks the success rate was 52% for X STOP patients and 10% for NON OP patients. At 6 months, the success rates were 52 and 9%, respectively, and at 1 year, 59 and 12%. The results of this prospective study indicate that the X STOP offers a significant improvement over non-operative therapies at 1 year with a success rate comparable to published reports for decompressive laminectomy, but with considerably lower morbidity.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

