A shortened instrument for literacy screening
- PMID: 14687263
- PMCID: PMC1494969
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2003.10651.x
A shortened instrument for literacy screening
Abstract
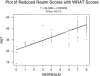
The Rapid Estimate of Adult Literacy in Medicine (REALM-R), a new 8-item instrument designed to rapidly screen patients for potential health literacy problems, was administered to 157 patients. The REALM-R was correlated with Wide Range Achievement Test-Revised (WRAT-R) (.64) and demonstrated a Cronbach's alpha of 0.91. The REALM-R identified 26 of 30 persons scoring more than 1 standard deviation below the mean on the WRAT-R, corresponding to a sixth grade reading level. The REALM-R identified a substantial number of people who scored poorly on the WRAT-R, and depending on further studies of validity and reliability, may offer a practical approach to identify patients at risk for health literacy problems in a clinical setting.
Figures
References
-
- Kirsh I, Jungenlut A, Jenjins L. Adult Literacy in America: A First Look at the Findings of the National Adult Literacy Survey. Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics, US Department of Education; 1993.
-
- Williams MV, Baker DW, Parker RM, Nurss JR. Relationship of functional health literacy to patients' knowledge of their chronic disease: a study of patients with hypertension and diabetes. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158:166–72. - PubMed
-
- Williams MV, Baker DW, Honig EG, Lee TM, Nowlan A. Inadequate literacy is a barrier to asthma knowledge and self care. Chest. 1998;114:1008–15. - PubMed
-
- Grosse RN, Auffrey C. Literacy and health status in developing countries. Annu Rev Public Health. 1989;10:281–97. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical