Optimization of Rolling-Circle Amplified Protein Microarrays for Multiplexed Protein Profiling
- PMID: 14688416
- PMCID: PMC521503
- DOI: 10.1155/S1110724303209268
Optimization of Rolling-Circle Amplified Protein Microarrays for Multiplexed Protein Profiling
Abstract
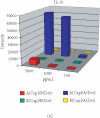
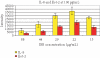
Protein microarray-based approaches are increasingly being used in research and clinical applications to either profile the expression of proteins or screen molecular interactions. The development of high-throughput, sensitive, convenient, and cost-effective formats for detecting proteins is a necessity for the effective advancement of understanding disease processes. In this paper, we describe the generation of highly multiplexed, antibody-based, specific, and sensitive protein microarrays coupled with rolling-circle signal amplification (RCA) technology. A total of 150 cytokines were simultaneously detected in an RCA sandwich immunoassay format. Greater than half of these proteins have detection sensitivities in the pg/ml range. The validation of antibody microarray with human serum indicated that RCA-based protein microarrays are a powerful tool for high-throughput analysis of protein expression and molecular diagnostics.
Figures
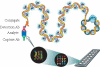






References
-
- MacBeath G, Schreiber S L. Printing proteins as microarrays for high-throughput function determination. Science. 2000;289(5485):1760–1763. - PubMed
-
- Zhu H, Bilgin M, Bangham R, et al. Global analysis of protein activities using proteome chips. Science. 2001;293(5537):2101–2105. - PubMed
-
- Petricoin E F. 3rd, Ardekani A M, Hitt B A, et al. Use of proteomic patterns in serum to identify ovarian cancer. Lancet. 2002;359(9306):572–577. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

