Emergence of oxacillinase-mediated resistance to imipenem in Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 14693513
- PMCID: PMC310167
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.1.15-22.2004
Emergence of oxacillinase-mediated resistance to imipenem in Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
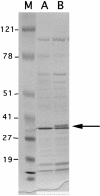
Klebsiella pneumoniae strain 11978 was isolated in Turkey in 2001 and was found to be resistant to all beta-lactams, including carbapenems. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli identified five beta-lactamases, including two novel oxacillinases. The beta-lactamase OXA-48 hydrolyzed imipenem at a high level and was remotely related (less than 46% amino acid identity) to the other oxacillinases. It hydrolyzed penicillins and imipenem but not expanded-spectrum cephalosporins. The bla(OXA-48) gene was plasmid encoded and not associated with an integron, in contrast to most of the oxacillinase genes. An insertion sequence, IS1999, was found immediately upstream of bla(OXA-48). Another plasmid that encoded a second oxacillinase gene, bla(OXA-47), located inside a class 1 integron was identified in K. pneumoniae 11978. OXA-47 had a narrow spectrum of hydrolysis activity and did not hydrolyze ceftazidime or imipenem, as is found for the beta-lactamase (OXA-1) to which it is related. In addition, beta-lactamases TEM-1 and SHV-2a were expressed from the same K. pneumoniae isolate. Analysis of the outer membrane proteins of this isolate revealed that it lacked a porin of ca. 36 kDa. Thus, the high-level resistance to beta-lactams of this clinical isolate resulted from peculiar beta-lactamases and modification of outer membrane proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Ardanuy, C., J. Linares, M. A. Dominguez, S. Hernandez-Alles, V. J. Benedi, and L. Martinez-Martinez. 1998. Outer membrane profiles of clonally related Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from clinical samples and activities of cephalosporins and carbapenems. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 42:1636-1640. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

