HB-EGF directs stromal cell polyploidy and decidualization via cyclin D3 during implantation
- PMID: 14697362
- PMCID: PMC4277116
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.09.019
HB-EGF directs stromal cell polyploidy and decidualization via cyclin D3 during implantation
Abstract
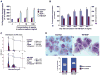
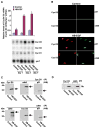
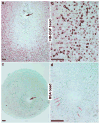
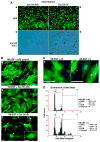
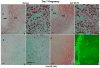
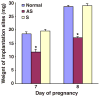
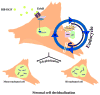
Stromal cell polyploidy is a unique phenomenon that occurs during uterine decidualization following embryo implantation, although the developmental mechanism still remains elusive. The general consensus is that the aberrant expression and altered functional activity of cell cycle regulatory molecules at two particular checkpoints G1 to S and G2 to M in the cell cycle play an important role in the development of cellular polyploidy. Despite the compelling evidence of intrinsic cell cycle alteration, it has been implicated that the development of cellular polyploidy may be controlled by specific actions of extracellular growth regulators. Here we show a novel role for heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) in the developmental process of stromal cell polyploidy in mice. HB-EGF, which is one of the earliest known molecular mediators of implantation in mice and humans, promotes stromal cell polyploidy via upregulation of cyclin D3. Adenoviral delivery of antisense cyclin D3 attenuates cyclin D3 expression and abrogates HB-EGF-induced stromal cell polyploidy in vitro and in vivo. Collectively, the results demonstrate that the regulation of stromal cell polyploidy and decidualization induced by HB-EGF depend on cyclin D3 induction.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander CM, Hansell EJ, Behrendtsen O, Flannery ML, Kishnani SP, Hawkes SP, Werb Z. Expression and function of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors at the maternal-embryonic boundary during mouse embryo implantation. Development. 1996;122:1723–1736. - PubMed
-
- Bahar R, O-Wang J, Kawamura K, Seimiya M, Wang Y, Hatano M, Okada S, Tokuhisa T, Watanabe T, Tagawa M. Growth retardation, polyploidy, and multinucleation induced by Clast3, a novel cell cycle-regulated protein. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:40012–40019. - PubMed
-
- Ballester A, Frampton J, Vilaboa N, Cales C. Heterologous expression of the transcriptional regulator escargot inhibits megakaryocytic endomitosis. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:43413–43418. - PubMed
-
- Carson DD, Bagchi I, Dey SK, Enders AC, Fazleabas AT, Lessey BA, Yoshinaga K. Embryo implantation. Dev Biol. 2000;223:217–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

