The alpha- and beta'-COP WD40 domains mediate cargo-selective interactions with distinct di-lysine motifs
- PMID: 14699056
- PMCID: PMC363058
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-10-0724
The alpha- and beta'-COP WD40 domains mediate cargo-selective interactions with distinct di-lysine motifs
Abstract
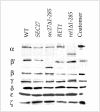
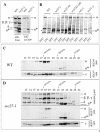
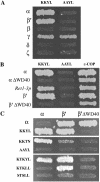
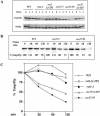
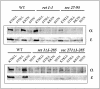
Coatomer is required for the retrieval of proteins from an early Golgi compartment back to the endoplasmic reticulum. The WD40 domain of alpha-COP is required for the recruitment of KKTN-tagged proteins into coatomer-coated vesicles. However, lack of the domain has only minor effects on growth in yeast. Here, we show that the WD40 domain of beta'-COP is required for the recycling of the KTKLL-tagged Golgi protein Emp47p. The protein is degraded more rapidly in cells with a point mutation in the WD40 domain of beta'-COP (sec27-95) or in cells lacking the domain altogether, whereas a point mutation in the Clathrin Heavy Chain Repeat (sec27-1) does not affect the turnover of Emp47p. Lack of the WD40 domain of beta'-COP has only minor effects on growth of yeast cells; however, absence of both WD40 domains of alpha- and beta'-COP is lethal. Two hybrid studies together with our analysis of the maturation of KKTN-tagged invertase and the turnover of Emp47p in alpha- and beta'-COP mutants suggest that the two WD40 domains of alpha- and beta'-COP bind distinct but overlapping sets of di-lysine signals and hence both contribute to recycling of proteins with di-lysine signals.
Figures


References
-
- Barlowe, C. (2003). Molecular recognition of cargo by the COP II complex: a most accommodating coat. Cell 114, 395-399. - PubMed
-
- Conibear, E., and Stevens, T.H. (1998). Multiple sorting pathways between the late Golgi and the vacuole in yeast. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1404, 211-230. - PubMed
-
- Cosson, P., and Letourneur, F. (1994). Coatomer interaction with di-lysine endoplasmic reticulum retention motifs. Science 263, 1629-1631. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson, J.G., and Jackson, C.L. (2000). Regulators and effectors of the ARF GTPases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12, 475-482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

