Sensitive and quantitative detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection by real-time nested polymerase chain reaction
- PMID: 14699465
- PMCID: PMC7107825
- DOI: 10.1086/380841
Sensitive and quantitative detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection by real-time nested polymerase chain reaction
Abstract
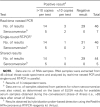
A quantitative, real-time, nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method, combining the high sensitivity of nested PCR with time-saving real-time instrumentation, was developed for large-scale screening for severe acute coronavirus (SARS) coronavirus. Forty-six clinical specimens were analyzed by this method, and results were compared with those obtained by conventional, single-round, real-time reverse-transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) performed in parallel. Of the 17 positive results, 2 identified by our method were not detected by single-round, real-time RT-PCR, which suggests that real-time nested PCR has the potential for increased sensitivity, leading to earlier detection of SARS.
Figures

Comment in
-
Crouching tiger, hidden dragon: the laboratory diagnosis of severe acute respiratory syndrome.Clin Infect Dis. 2004 Jan 15;38(2):297-9. doi: 10.1086/380848. Epub 2003 Dec 18. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 14699466 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrom. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1953–66. - PubMed
-
- Drosten C, Gunther S, Preiser W, et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrom. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1967–76. - PubMed
-
- Berg J, Nagl V, Muhlbauer G, Stekel H. Single-tube two-round polymerase chain reaction using the LightCycler instrumen. J Clin Virol. 2001;20:71–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

